Neuroprotective effect of a formula, moschus combined with borneolum synthcticum, from traditional chinese medicine on ischemia stroke in rats
- PMID: 24782904
- PMCID: PMC3982284
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/157938
Neuroprotective effect of a formula, moschus combined with borneolum synthcticum, from traditional chinese medicine on ischemia stroke in rats
Abstract
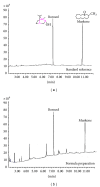
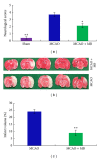
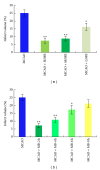
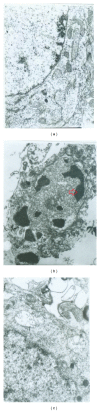
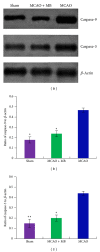
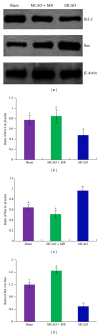
Moschus compatible with borneolum synthcticum is a well-known herb pair in Traditional Chinese Medicine and the present study aims to assess the neuroprotective effect of a formula composed of this herb pair on ischemia stroke in rats. The middle cerebral artery occlusion model of focal cerebral ischemia in rat was performed by using intraluminal suture method. The behavioral scores, infarct volume, and neuron ultrastructure of model and formula-treated rats were investigated after the 2 h of ischemia and 24 h of reperfusion. Meanwhile the expression levels of caspase-3, caspase-9, Bcl-2, and Bax were measured by western blot analysis. The formula treatment showed obvious neuroprotective effect according to significant decrease of the neurological scores (P < 0.01) and the infarct volumes (P < 0.05) when compared to the MCAO group. We also observed that this formula had antiapoptosis activity on neuron cell under electron microscope. Furthermore, our result supported the idea that pro- and postadministration of this formula had an antiapoptosis effect by decreasing remarkably the expression of caspase-3 and caspase-9 (P < 0.05) as well as increasing significantly the ratio of Bcl-2 to Bax (P < 0.01). All evidences demonstrated the neuroprotective effect of this formula on ischemia stroke due to decrease of brain infract volume and modulation of the expression of apoptosis-related proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An-Gong-Niu-Huang Wan protects against cerebral ischemia induced apoptosis in rats: up-regulation of Bcl-2 and down-regulation of Bax and caspase-3.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 28;154(1):156-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.057. Epub 2014 Mar 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24690773
-
Protective effects of Tongxinluo on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury related to Connexin 43/Calpain II/Bax/Caspase-3 pathway in rat.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 23;198:148-157. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28065778
-
Study on drug property differences of shexiang (moschus) and bingpian (borneolum synthcticum) based on analysis of biothermodynamics.J Tradit Chin Med. 2011 Mar;31(1):21-6. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(11)60005-8. J Tradit Chin Med. 2011. PMID: 21563501
-
Neuroprotective effect and mechanism of Mu-Xiang-You-Fang on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Nov 4;192:140-147. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.016. Epub 2016 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27396346
-
Neuroprotective effects of different frequency preconditioning exercise on neuronal apoptosis after focal brain ischemia in rats.Neurol Res. 2019 Jun;41(6):510-518. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2019.1580458. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Neurol Res. 2019. PMID: 30822224
Cited by
-
Shexiang Baoxin Pill, a Formulated Chinese Herbal Mixture, Induces Neuronal Differentiation of PC12 Cells: A Signaling Triggered by Activation of Protein Kinase A.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 9;10:1130. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01130. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31649530 Free PMC article.
-
XingNaoJing, prescription of traditional Chinese medicine, prevents autophagy in experimental stroke by repressing p53-DRAM pathway.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015 Oct 19;15:377. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0882-2. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015. PMID: 26481508 Free PMC article.
-
Xingnaojing for Moderate-to-severe Acute ischemic Stroke (XMAS): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Oct 16;18(1):479. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2222-y. Trials. 2017. PMID: 29037226 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Essential Role of Chinese Medicines in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Oct;25(10):723-727. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-2708-4. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31782008
-
Xingnaojing Injection Protects against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via PI3K/Akt-Mediated eNOS Phosphorylation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Aug 8;2018:2361046. doi: 10.1155/2018/2361046. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30158991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics: 2009 update. A report from the American heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119(3):480–486. - PubMed
-
- Candelario-Jalil E. Injury and repair mechanisms in ischemic stroke: considerations for the development of novel neurotherapeutics. Current Opinion in Investigational Drugs. 2009;10(7):644–654. - PubMed
-
- Turner R, Vink R. Inhibition of neurogenic inflammation as a novel treatment for ischemic stroke. Timely Topics in Medicine: Cardiovascular diseases. 2007;11:E24–E27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

