Serum cystatin C as a marker of renal function in critically ill patients with normal serum creatinine
- PMID: 24783172
- PMCID: PMC3997954
- DOI: 10.5812/numonthly.15224
Serum cystatin C as a marker of renal function in critically ill patients with normal serum creatinine
Abstract
Background: Serum creatinine as a classic marker of renal function has several limitations in the detection of renal dysfunction.
Objectives: This study assessed the validity of serum cystatin C as a marker of renal function in critically ill patients with normal serum creatinine.
Patients and methods: Eighty adult patients referred to intensive care units with serum creatinine levels < 1.5 mg/dL and without hemodynamic instability were chosen and their serum creatinine and cystatin C levels were measured. A 24-hour urine sample was collected to calculate creatinine clearance (Ccr). Renal dysfunction was defined as Ccr < 80 mL/min/1.73 m(2).
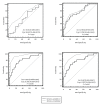
Results: There were significant correlations between measured Ccr and 1/serum creatinine (R = 0.51, P < 0.001) and 1/serum cystatin C (R = 0.25, P = 0.028). The difference between false negative rates of serum creatinine (93.33%) and cystatin C (80%) in the detection of renal dysfunction was significant (P = 0.032). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis illustrated that area under the curve of serum creatinine and cystatin C for detecting renal dysfunction were 0.711 and 0.607, respectively; however, this difference was not significant (P = 0.222).
Conclusions: Our data demonstrated that serum cystatin C is not superior to serum creatinine in the early detection of renal dysfunction in critically ill patients.
Keywords: Acute Kidney Injury; Creatinine; Critically Ill; Cystatin C; Patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum cystatin C concentration as a marker of acute renal dysfunction in critically ill patients.Crit Care. 2005 Apr;9(2):R139-43. doi: 10.1186/cc3044. Epub 2005 Feb 7. Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 15774046 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum cystatin C in critically ill children with acute kidney injury.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2015 Jun;16(5):e125-31. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000403. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2015. PMID: 25838149
-
Cystatin C and beta2-microglobulin: markers of glomerular filtration in critically ill children.Crit Care. 2007;11(3):R59. doi: 10.1186/cc5923. Crit Care. 2007. PMID: 17519026 Free PMC article.
-
Serum cystatin C concentration compared with other markers of glomerular filtration rate in the old old.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002 Jul;50(7):1278-82. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50317.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002. PMID: 12133025
-
Serum cystatin is a useful marker for the diagnosis of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: prospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2016 Sep 13;17(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0346-z. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27624749 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cystatin C Falsely Underestimated GFR in a Critically Ill Patient with a New Diagnosis of AIDS.Case Rep Nephrol. 2016;2016:9349280. doi: 10.1155/2016/9349280. Epub 2016 May 17. Case Rep Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27293926 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: From Past to Present Definition and Diagnosis.Life (Basel). 2025 Aug 6;15(8):1249. doi: 10.3390/life15081249. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic assessment of vancomycin in critically ill patients and nephrotoxicity prediction using individualized pharmacokinetic parameters.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 24;13:912202. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.912202. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36091788 Free PMC article.
-
[Renal replacement therapy in the intensive care unit].Internist (Berl). 2014 Nov;55(11):1278-87. doi: 10.1007/s00108-014-3508-8. Internist (Berl). 2014. PMID: 25315764 Review. German.
-
Detection of cystatin C biomarker for clinical measurement of renal disease by developed ELISA diagnostic kits.J Transl Med. 2014 Sep 12;12:205. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-12-205. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25216761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellum JA, Levin N, Bouman C, Lameire N. Developing a consensus classification system for acute renal failure. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2002;8(6):509–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
