Precursor lesions for sporadic pancreatic cancer: PanIN, IPMN, and MCN
- PMID: 24783207
- PMCID: PMC3982269
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/474905
Precursor lesions for sporadic pancreatic cancer: PanIN, IPMN, and MCN
Abstract
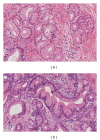
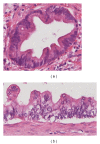
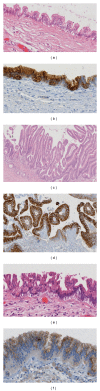
Pancreatic cancer is still a dismal disease. The high mortality rate is mainly caused by the lack of highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tools, and most of the patients are diagnosed in an advanced and incurable stage. Knowledge about precursor lesions for pancreatic cancer has grown significantly over the last decade, and nowadays we know that mainly three lesions (PanIN, and IPMN, MCN) are responsible for the development of pancreatic cancer. The early detection of these lesions is still challenging but provides the chance to cure patients before they might get an invasive pancreatic carcinoma. This paper focuses on PanIN, IPMN, and MCN lesions and reviews the current level of knowledge and clinical measures.
Figures


References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2012;62(1):10–29. - PubMed
-
- Winter JM, Cameron JL, Campbell KA, et al. 1423 Pancreaticoduodenectomies for pancreatic cancer: a single-institution experience. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery . 2006;10(9):1199–1210. - PubMed
-
- Oettle H, Post S, Neuhaus P, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine vs observation in patients undergoing curative-intent resection of pancreatic cancer: a randomized controlled trial. The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2007;297(3):267–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

