Emission tuning of fluorescent kinase inhibitors: conjugation length and substituent effects
- PMID: 24784897
- PMCID: PMC4049246
- DOI: 10.1021/jo500520x
Emission tuning of fluorescent kinase inhibitors: conjugation length and substituent effects
Abstract
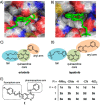
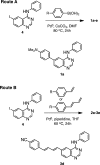
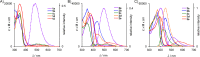
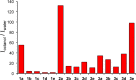
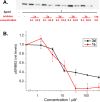
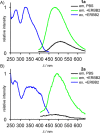
Fluorescent N-phenyl-4-aminoquinazoline probes targeting the ATP-binding pocket of the ERBB family of receptor tyrosine kinases are reported. Extension of the aromatic quinazoline core with fluorophore "arms" through substitution at the 6- position of the quinazoline core with phenyl, styryl, and phenylbutadienyl moieties was predicted by means of TD-DFT calculations to produce probes with tunable photoexcitation energies and excited states possessing charge-transfer character. Optical spectroscopy identified several synthesized probes that are nonemissive in aqueous solutions and exhibit emission enhancements in solvents of low polarity, suggesting good performance as turn-on fluorophores. Ligand-induced ERBB2 phosphorylation assays demonstrate that despite chemical modification to the quinazoline core these probes still function as ERBB2 inhibitors in MCF7 cells. Two probes were found to exhibit ERBB2-induced fluorescence, demonstrating the utility of these probes as turn-on, fluoroescent kinase inhibitors.
Figures



References
-
- Davis M. I.; Hunt J. P.; Herrgard S.; Ciceri P.; Wodicka L. M.; Pallares G.; Hocker M.; Treiber D. K.; Zarrinkar P. P. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1046–1051. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

