Predictors of early readmission among patients 40 to 64 years of age hospitalized for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- PMID: 24784958
- PMCID: PMC4225809
- DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201310-358OC
Predictors of early readmission among patients 40 to 64 years of age hospitalized for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Abstract
Rationale: Various causes can contribute to the high rates of readmission among patients hospitalized with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Objectives: To determine the frequency and predictors of early readmission among patients aged 40-64 years, hospitalized with COPD.
Methods: In a retrospective cohort study, using a large national commercial insurance database, we obtained the clinical information within 12 months of the index hospitalization and 30 days after discharge.
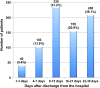
Measurements and main results: Primary outcome was early readmission, defined as hospitalization within 30 days of discharge. We categorized predictor variables as patient, provider, and system factors, and compared these variables between patients readmitted and those not readmitted. Logistic regression was used for multivariable analysis. Of 8,263 patients who met the inclusion criteria, 741 (8.9%) had early readmission. Multivariable analysis showed patient factors (male, history of heart failure, lung cancer, osteoporosis, and depression), provider factors (no prior prescription of statin within 12 mo of the index hospitalization and no prescription of short-acting bronchodilator, oral steroid and antibiotic on discharge), and system factors (length of stay, <2 or >5 d and lack of follow-up visit after discharge) were associated with early readmission among patients hospitalized with COPD. The C-statistic of the model including patient characteristics was 0.677 (95% confidence interval, 0.656-0.697), which was improved to 0.717 (95% confidence interval, 0.702-0.732) after addition of provider- and system-based factors.
Conclusions: One of 11 patients hospitalized with COPD is readmitted within 30 days of discharge. Provider and system factors are important modifiable risk factors of early readmission.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; follow-up visit; hospital readmission.
Figures
Comment in
References
-
- Krumholz HM, Merrill AR, Schone EM, Schreiner GC, Chen J, Bradley EH, Wang Y, Wang Y, Lin Z, Straube BM, et al. Patterns of hospital performance in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure 30-day mortality and readmission. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2009;2:407–413. - PubMed
-
- Krumholz HM, Normand SL, Spertus JA, Shahian DM, Bradley EH. Measuring performance for treating heart attacks and heart failure: the case for outcomes measurement. Health Aff (Millwood) 2007;26:75–85. - PubMed
-
- Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare and Medicaid ServicesHospital Compare, 2014. Available from: http://www.medicare.gov/hospitalcompare/search.html
-
- Jencks SF, Williams MV, Coleman EA. Rehospitalizations among patients in the Medicare fee-for-service program. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:1418–1428. - PubMed
-
- Camberg LC, Smith NE, Beaudet M, Daley J, Cagan M, Thibault G. Discharge destination and repeat hospitalizations. Med Care. 1997;35:756–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

