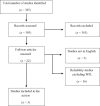
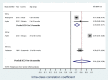
The reliability of weight-for-length/height Z scores in children
- PMID: 24785183
- PMCID: PMC4282477
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.12124
The reliability of weight-for-length/height Z scores in children
Abstract
The World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends weight-for-length/height (WFL/H), represented as a Z score for diagnosing acute malnutrition among children aged 0 to 60 months. Under controlled conditions, weight, height and length measurements have high degree of reliability. However, the reliability when combined into a WFL/H Z score, in all settings is unclear. We conducted a systematic review of published studies assessing the reliability of WFL/Hz on PubMed and Google scholar. Studies were included if they presented reliability scores for the derived index of WFL/Hz, for children under 5 years. Meta-analysis was conducted for a pooled estimate of reliability overall, and for children above and below 24 months old. Twenty six studies on reliability of anthropometry were identified but only three, all community-based studies, reported reliability scores for WFL/Hz. The overall pooled intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) estimate for WFL/Hz among children aged 0 to 60 months was 0.81 (95% CI 0.64 to 0.99). Among children aged less than 24 months the pooled ICC estimate from two studies was 0.72 (95% CI 0.67 to 0.77) while the estimate reported for children above 24 months from one study was 0.97 (95% CI 0.97 to 0.99). Although WFL/Hz is recommended for diagnosis of acute under nutrition among children below 5 years, information on its reliability in all settings is sparse. In community settings, reliability of WFL/Hz is considerably lower than for absolute measures of weight and length/height, especially in younger children. The reliability of WFL/Hz needs further evaluation.
Keywords: children; reliability; weight-for-height; weight-for-length.
© 2014 The Authors. Maternal & Child Nutrition published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ayele B., Aemere A., Gebre T., Tadesse Z., Stoller N.E., See C.W. et al (2012a) Reliability of measurements performed by community‐drawn anthropometrists from rural Ethiopia . [Online]. Available at: http://www.plosone.org/annotation/listThread.action?root=50461 (Accessed 1 July 2013). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayele B., Aemere A., Gebre T., Tadesse Z., Stoller N.E., See C.W. et al (2012b) Reliability of measurements performed by community‐drawn anthropometrists from rural Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 7, e30345 [Online]. Available at: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22291939 (Accessed 30 July 2012). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhushan V. & Paneth N. (1991) The reliability of neonatal head circumference measurement. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 44, 1027–1035. - PubMed
-
- Black R.E., Allen L.H., Bhutta Z.A., Caulfield L.E., De Onis M., Ezzati M. et al (2008) Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 371, 243–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical