Ecological effects of the invasive giant madagascar day gecko on endemic mauritian geckos: applications of binomial-mixture and species distribution models
- PMID: 24785293
- PMCID: PMC4005729
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088798
Ecological effects of the invasive giant madagascar day gecko on endemic mauritian geckos: applications of binomial-mixture and species distribution models
Abstract
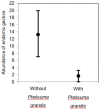
The invasion of the giant Madagascar day gecko Phelsuma grandis has increased the threats to the four endemic Mauritian day geckos (Phelsuma spp.) that have survived on mainland Mauritius. We had two main aims: (i) to predict the spatial distribution and overlap of P. grandis and the endemic geckos at a landscape level; and (ii) to investigate the effects of P. grandis on the abundance and risks of extinction of the endemic geckos at a local scale. An ensemble forecasting approach was used to predict the spatial distribution and overlap of P. grandis and the endemic geckos. We used hierarchical binomial mixture models and repeated visual estimate surveys to calculate the abundance of the endemic geckos in sites with and without P. grandis. The predicted range of each species varied from 85 km2 to 376 km2. Sixty percent of the predicted range of P. grandis overlapped with the combined predicted ranges of the four endemic geckos; 15% of the combined predicted ranges of the four endemic geckos overlapped with P. grandis. Levin's niche breadth varied from 0.140 to 0.652 between P. grandis and the four endemic geckos. The abundance of endemic geckos was 89% lower in sites with P. grandis compared to sites without P. grandis, and the endemic geckos had been extirpated at four of ten sites we surveyed with P. grandis. Species Distribution Modelling, together with the breadth metrics, predicted that P. grandis can partly share the equivalent niche with endemic species and survive in a range of environmental conditions. We provide strong evidence that smaller endemic geckos are unlikely to survive in sympatry with P. grandis. This is a cause of concern in both Mauritius and other countries with endemic species of Phelsuma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Mack RN, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM, Evans H, Clout M, et al. (2000) Biotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control. Ecol Appl 10: 689–710 10.2307/2641039 - DOI
-
- O'Dowd DJ, Green PT, Lake PS (2003) Invasional ‘meltdown’ on an oceanic island. Ecol Lett 6: 812–817 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00512.x - DOI
-
- Charles H, Dukes JS (2007) Impacts of invasive species on ecosystem services. In: Nentwig DW, editor. Biological invasions. Berlin: Springer. pp. 217–237.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

