Epidermal nerve fiber density, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial haplogroups in HIV-infected Thais initiating therapy
- PMID: 24785954
- PMCID: PMC4427899
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000297
Epidermal nerve fiber density, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial haplogroups in HIV-infected Thais initiating therapy
Abstract
Objective: We explored associations between mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroups, epidermal nerve fiber density (ENFD), and HIV-associated sensory neuropathy (HIV-SN) in a randomized trial of Thai patients initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART).
Design: The South East Asia Research Collaboration with Hawaii 003 study evaluated toxicity of nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (stavudine vs. zidovudine vs. tenofovir). We present secondary analyses of mtDNA haplogroups and ENFD changes.
Methods: ENFD, peripheral blood mononuclear cell mitochondrial complex I and IV, and 8-oxo-deoxyguanine (8-oxo-dG) were quantified. Peripheral blood mononuclear cell mtDNA sequences were obtained for haplogroup determination. Multivariate regression of ENFD change was performed.
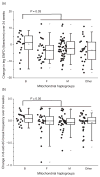
Results: Paired ENFD was available from 118 patients. Median age, CD4 cell count, and height at entry were 34 years, 172 cells/μl, and 162 cm, respectively. Major haplogroups included M (42%), F (21%), and B (16%). Baseline ENFD, CD4 cell count, randomized ART, and biomarkers did not differ by haplogroup. Haplogroup B patients were older (P=0.02) at baseline, and had an increase in median ENFD (+1.5 vs. -2.9 fibers/mm; P=0.03) and 8-oxo-dG break frequency (+0.05 vs. 0.00; P=0.05) compared to other haplogroups. In a multivariate model, haplogroup B was associated with increased ENFD (β=3.5, P=0.009) at week 24, whereas older age (P=0.02), higher baseline CD4 cell count, (P=0.03), higher complex I level (P=0.03), and higher ENFD (P<0.001) at baseline were all associated with decreased ENFD. Three of the six HIV-SN cases were haplogroup B (P=0.05).
Conclusions: Thai persons belonging to mtDNA haplogroup B had increased ENFD and 8-oxo-dG on ART, and were more likely to develop HIV-SN. These results suggest that mtDNA variation influences early oxidative damage and ENFD changes.
Conflict of interest statement
N.P. serves as an academic advisory committee member of the Thai Government Pharmaceutical Organization.
J.A. has received honoraria and speaker’s fee from Gilead. She serves as an academic advisory committee member of the Thai Government Pharmaceutical Organization.
J.C.M. is an unpaid consultant for Biogen-Idec and Allergan, has received research funding for clinical trials from Pfizer and Biogen-Idec, and holds stock options in Revelare and Gliamed for serving on Scientific Advisory Boards.
C.M.S. received research and training funding support from Gilead Sciences, ViiV and Mitosciences. She is also on the speaker’s bureau for ViiV.
T.H. has served as PI of research grants to Vanderbilt University from Merck & Co.
For the remaining authors no conflicts were declared.
Figures
References
-
- Keswani SC, Pardo CA, Cherry CL, Hoke A, McArthur JC. HIV-associated sensory neuropathies. AIDS. 2002;16:2105–2117. - PubMed
-
- Desakorn V, Karmacharya BM, Thanachartwet V, Kyaw NL, Tansuphaswadikul S, Sahassananda D, et al. Effectiveness of fixed-dose combination stavudine, lamivudine and nevirapine (GPO-VIR) for treatment of naive HIV patients in Thailand: a 3-year follow-up. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2011;42:1414–1422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

