Recent advances in bacteria identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using nanomaterials as affinity probes
- PMID: 24786089
- PMCID: PMC4057671
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15057266
Recent advances in bacteria identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry using nanomaterials as affinity probes
Abstract
Identifying trace amounts of bacteria rapidly, accurately, selectively, and with high sensitivity is important to ensuring the safety of food and diagnosing infectious bacterial diseases. Microbial diseases constitute the major cause of death in many developing and developed countries of the world. The early detection of pathogenic bacteria is crucial in preventing, treating, and containing the spread of infections, and there is an urgent requirement for sensitive, specific, and accurate diagnostic tests. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) is an extremely selective and sensitive analytical tool that can be used to characterize different species of pathogenic bacteria. Various functionalized or unmodified nanomaterials can be used as affinity probes to capture and concentrate microorganisms. Recent developments in bacterial detection using nanomaterials-assisted MALDI-MS approaches are highlighted in this article. A comprehensive table listing MALDI-MS approaches for identifying pathogenic bacteria, categorized by the nanomaterials used, is provided.
Figures
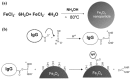

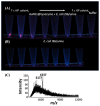
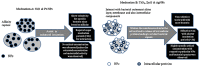
References
-
- Ivnitski D., Abdel-Hamid I., Atanasov P., Wilkins E. Biosensors for detection of pathogenic bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1999;14:599–624. - PubMed
-
- WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. [accessed on 7 May 2014]. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/dwq/guidelines/en/
-
- Jahid I.K., Ha S.-D. A review of microbial biofilms of produce: Future challenge to food safety. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012;21:299–316.
-
- Velusamy V., Arshak K., Korostynska O., Oliwa K., Adley C. An overview of foodborne pathogen detection: In the perspective of biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010;28:232–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

