ANG II promotes IGF-IIR expression and cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting HSF1 via JNK activation and SIRT1 degradation
- PMID: 24786827
- PMCID: PMC4085534
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.46
ANG II promotes IGF-IIR expression and cardiomyocyte apoptosis by inhibiting HSF1 via JNK activation and SIRT1 degradation
Abstract
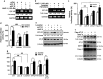
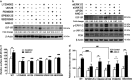
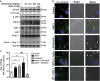
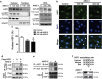
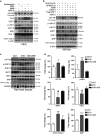
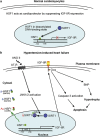
Hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis are major characteristics of early-stage heart failure. Our previous studies found that the activation of insulin-like growth factor receptor II (IGF-IIR) signaling was critical for hypertensive angiotensin II (ANG II)-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. However, the detailed mechanism by which ANG II regulates IGF-IIR in heart cells remains elusive. In this study, we found that ANG II activated its downstream kinase JNK to increase IGF-IIR expression through the ANG II receptor angiotensin type 1 receptor. JNK activation subsequently led to sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) degradation via the proteasome, thus preventing SIRT1 from deacetylating heat-shock transcription factor 1 (HSF1). The resulting increase in the acetylation of HSF1 impaired its ability to bind to the IGF-IIR promoter region (nt -748 to -585). HSF1 protected cardiomyocytes by acting as a repressor of IGF-IIR gene expression, and ANG II diminished this HSF1-mediated repression through enhanced acetylation, thus activating the IGF-IIR apoptosis pathway. Taken together, these results suggest that HSF1 represses IGF-IIR gene expression to protect cardiomyocytes. ANG II activates JNK to degrade SIRT1, resulting in HSF1 acetylation, which induces IGF-IIR expression and eventually results in cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis. HSF1 could be a valuable target for developing treatments for cardiac diseases in hypertensive patients.
Figures


References
-
- George AJ, Thomas WG, Hannan RD. The renin–angiotensin system and cancer: old dog, new tricks. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:745–759. - PubMed
-
- Herichova I, Szantoova K. Renin–angiotensin system: upgrade of recent knowledge and perspectives. Endocr Regul. 2013;47:39–52. - PubMed
-
- Mehta PK, Griendling KK. Angiotensin II cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292:C82–C97. - PubMed
-
- Hunyady L, Catt KJ. Pleiotropic AT1 receptor signaling pathways mediating physiological and pathogenic actions of angiotensin II. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:953–970. - PubMed
-
- Braulke T. Type-2 IGF receptor: a multi-ligand binding protein. Horm Metab Res. 1999;31 (2–3:242–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

