Reversion of apoptotic resistance of TP53-mutated Burkitt lymphoma B-cells to spindle poisons by exogenous activation of JNK and p38 MAP kinases
- PMID: 24787013
- PMCID: PMC4047855
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.150
Reversion of apoptotic resistance of TP53-mutated Burkitt lymphoma B-cells to spindle poisons by exogenous activation of JNK and p38 MAP kinases
Abstract
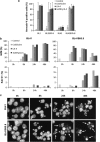
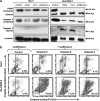
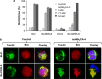
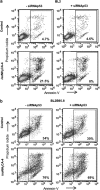
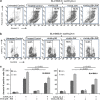
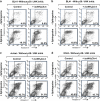
Defects in apoptosis are frequently the cause of cancer emergence, as well as cellular resistance to chemotherapy. These phenotypes may be due to mutations of the tumor suppressor TP53 gene. In this study, we examined the effect of various mitotic spindle poisons, including the new isocombretastatin derivative isoNH2CA-4 (a tubulin-destabilizing molecule, considered to bind to the colchicine site by analogy with combretastatin A-4), on BL (Burkitt lymphoma) cells. We found that resistance to spindle poison-induced apoptosis could be reverted in tumor protein p53 (TP53)-mutated cells by EBV (Epstein Barr virus) infection. This reversion was due to restoration of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, as assessed by relocation of the pro-apoptotic molecule Bax to mitochondria, loss of mitochondrial integrity and activation of the caspase cascade with PARP (poly ADP ribose polymerase) cleavage. EBV sensitized TP53-mutated BL cells to all spindle poisons tested, including vincristine and taxol, an effect that was systematically downmodulated by pretreatment of cells with inhibitors of p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinases. Exogenous activation of p38 and JNK pathways by dihydrosphingosine reverted resistance of TP53-mutated BL cells to spindle poisons. Dihydrosphingosine treatment of TP53-deficient Jurkat and K562 cell lines was also able to induce cell death. We conclude that activation of p38 and JNK pathways may revert resistance of TP53-mutated cells to spindle poisons. This opens new perspectives for developing alternative therapeutic strategies when the TP53 gene is inactivated.
Figures

References
-
- Henson PM, Bratton DL, Fadok VA. Apoptotic cell removal. Curr Biol. 2001;11:R795–R805. - PubMed
-
- Green DR, Kroemer G. The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 2004;305:626–629. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C. Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:99–163. - PubMed
-
- LaCasse EC, Mahoney DJ, Cheung HH, Plenchette S, Baird S, Korneluk RG. IAP-targeted therapies for cancer. Oncogene. 2008;27:6252–6275. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

