Dissecting vancomycin-intermediate resistance in staphylococcus aureus using genome-wide association
- PMID: 24787619
- PMCID: PMC4040999
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evu092
Dissecting vancomycin-intermediate resistance in staphylococcus aureus using genome-wide association
Abstract
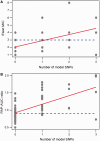
Vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) is currently defined as having minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 4-8 µg/ml. VISA evolves through changes in multiple genetic loci with at least 16 candidate genes identified in clinical and in vitro-selected VISA strains. We report a whole-genome comparative analysis of 49 vancomycin-sensitive S. aureus and 26 VISA strains. Resistance to vancomycin was determined by broth microdilution, Etest, and population analysis profile-area under the curve (PAP-AUC). Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of 55,977 single-nucleotide polymorphisms identified in one or more strains found one highly significant association (P = 8.78 E-08) between a nonsynonymous mutation at codon 481 (H481) of the rpoB gene and increased vancomycin MIC. Additionally, we used a database of public S. aureus genome sequences to identify rare mutations in candidate genes associated with VISA. On the basis of these data, we proposed a preliminary model called ECM+RMCG for the VISA phenotype as a benchmark for future efforts. The model predicted VISA based on the presence of a rare mutation in a set of candidate genes (walKR, vraSR, graSR, and agrA) and/or three previously experimentally verified mutations (including the rpoB H481 locus) with an accuracy of 81% and a sensitivity of 73%. Further, the level of resistance measured by both Etest and PAP-AUC regressed positively with the number of mutations present in a strain. This study demonstrated 1) the power of GWAS for identifying common genetic variants associated with antibiotic resistance in bacteria and 2) that rare mutations in candidate gene, identified using large genomic data sets, can also be associated with resistance phenotypes.
Keywords: bacteria; genomics; phylogeny; whole-genome sequencing.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Molecular Biology and Evolution.
Figures



References
-
- Breiman L. Random forests. Machine Learn. 2001;45:5–32.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

