Global microRNA depletion suppresses tumor angiogenesis
- PMID: 24788094
- PMCID: PMC4035535
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.239681.114
Global microRNA depletion suppresses tumor angiogenesis
Abstract
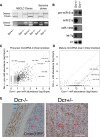
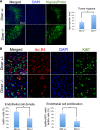
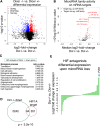
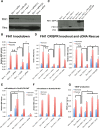
MicroRNAs delicately regulate the balance of angiogenesis. Here we show that depletion of all microRNAs suppresses tumor angiogenesis. We generated microRNA-deficient tumors by knocking out Dicer1. These tumors are highly hypoxic but poorly vascularized, suggestive of deficient angiogenesis signaling. Expression profiling revealed that angiogenesis genes were significantly down-regulated as a result of the microRNA deficiency. Factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1), FIH1, is derepressed under these conditions and suppresses HIF transcription. Knocking out FIH1 using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome engineering reversed the phenotypes of microRNA-deficient cells in HIF transcriptional activity, VEGF production, tumor hypoxia, and tumor angiogenesis. Using multiplexed CRISPR/Cas9, we deleted regions in FIH1 3' untranslated regions (UTRs) that contain microRNA-binding sites, which derepresses FIH1 protein and represses hypoxia response. These data suggest that microRNAs promote tumor responses to hypoxia and angiogenesis by repressing FIH1.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; Dicer; angiogenesis; gene regulation; hypoxia; microRNA.
© 2014 Chen et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


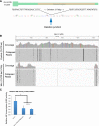
Comment in
-
Hypoxia: micro changes.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Jun;14(6):382-3. doi: 10.1038/nrc3754. Epub 2014 May 15. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24827507 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ, Mills AA, Elledge SJ, Anderson KV, Hannon GJ 2003. Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet 35: 215–217 - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME 1999. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868 - PubMed
-
- Calin GA, Croce CM 2006. MicroRNA–cancer connection: the beginning of a new tale. Cancer Res 66: 7390–7394 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 EB006365/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB006365/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA14051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- EB016101-01A1/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB016101/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA133404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA151884/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- P01 CA042063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133404/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 MH100706/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
