Rap1b in smooth muscle and endothelium is required for maintenance of vascular tone and normal blood pressure
- PMID: 24790136
- PMCID: PMC4224284
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303678
Rap1b in smooth muscle and endothelium is required for maintenance of vascular tone and normal blood pressure
Abstract
Objective: Small GTPase Ras-related protein 1 (Rap1b) controls several basic cellular phenomena, and its deletion in mice leads to several cardiovascular defects, including impaired adhesion of blood cells and defective angiogenesis. We found that Rap1b(-/-) mice develop cardiac hypertrophy and hypertension. Therefore, we examined the function of Rap1b in regulation of blood pressure.
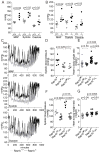
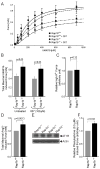
Approach and results: Rap1b(-/-) mice developed cardiac hypertrophy and elevated blood pressure, but maintained a normal heart rate. Correcting elevated blood pressure with losartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist, alleviated cardiac hypertrophy in Rap1b(-/-) mice, suggesting a possibility that cardiac hypertrophy develops secondary to hypertension. The indices of renal function and plasma renin activity were normal in Rap1b(-/-) mice. Ex vivo, we examined whether the effect of Rap1b deletion on smooth muscle-mediated vessel contraction and endothelium-dependent vessel dilation, 2 major mechanisms controlling basal vascular tone, was the basis for the hypertension. We found increased contractility on stimulation with a thromboxane analog or angiotensin II or phenylephrine along with increased inhibitory phosphorylation of myosin phosphatase under basal conditions consistent with elevated basal tone and the observed hypertension. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent relaxation in response to Rap1 activator, Epac, was decreased in vessels from Rap1b(-/-) mice. Defective endothelial release of dilatory nitric oxide in response to elevated blood flow leads to hypertension. We found that nitric oxide-dependent vasodilation was significantly inhibited in Rap1b-deficient vessels.
Conclusions: This is the first report to indicate that Rap1b in both smooth muscle and endothelium plays a key role in maintaining blood pressure by controlling normal vascular tone.
Keywords: relaxation; signal transduction; vasodilation.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL, Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT, Jr, Roccella EJ. The seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure: The jnc 7 report. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M, Narumiya S. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature. 1997;389:990–994. - PubMed
-
- Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Ca 2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin ii: Modulated by g proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiological Reviews. 2003;83:1325–1358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL077707/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL07707/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK088905/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL089471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL029587/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096859/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL29587/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK088905/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK96859/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM086457/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL089471/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL096647/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111582/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111392/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL111583/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL096647/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM86457/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

