Electrosprayed core-shell solid dispersions of acyclovir fabricated using an epoxy-coated concentric spray head
- PMID: 24790437
- PMCID: PMC3998863
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S59516
Electrosprayed core-shell solid dispersions of acyclovir fabricated using an epoxy-coated concentric spray head
Abstract
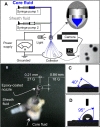
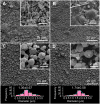
A novel structural solid dispersion (SD) taking the form of core-shell microparticles for poorly water-soluble drugs is reported for the first time. Using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) as a hydrophilic polymer matrix, the SDs were fabricated using coaxial electrospraying (characterized by an epoxy-coated concentric spray head), although the core fluids were unprocessable using one-fluid electrospraying. Through manipulating the flow rates of the core drug-loaded solutions, two types of core-shell microparticles with tunable drug contents were prepared. They had average diameters of 1.36±0.67 and 1.74±0.58 μm, and were essentially a combination of nanocomposites with the active ingredient acyclovir (ACY) distributed in the inner core, and the sweeter sucralose and transmembrane enhancer sodium dodecyl sulfate localized in the outer shell. Differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction results demonstrated that ACY, sodium dodecyl sulfate, and sucralose were well distributed in the PVP matrix in an amorphous state because of favorable second-order interactions. In vitro dissolution and permeation studies showed that the core-shell microparticle SDs rapidly freed ACY within 1 minute and promoted nearly eightfold increases in permeation rate across the sublingual mucosa compared with raw ACY powders.
Keywords: coaxial electrospraying; core–shell microparticle; epoxy-coated spray head; poorly water-soluble drug; solid dispersion.
Figures







References
-
- Bikiaris DN. Solid dispersions, part II: new strategies in manufacturing methods for dissolution rate enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(12):1663–1680. - PubMed
-
- Tran PH, Tran TT, Park JB, Lee BJ. Controlled release systems containing solid dispersions: strategies and mechanisms. Pharm Res. 2011;28(10):2353–2378. - PubMed
-
- Brettmann B, Bell E, Myerson A, Trout B. Solid-state NMR characterization of high-loading solid solutions of API and excipients formed by electrospinning. J Pharm Sci. 2012;101(4):1538–1545. - PubMed
-
- Vasconcelos T, Sarmento B, Costa P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water-soluble drugs. Drug Discov Today. 2007;12(23–24):1068–1075. - PubMed
-
- Pasquali I, Bettini R, Giordano F. Supercritical fluid technologies: an innovative approach for manipulating the solid-state of pharmaceuticals. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(3):399–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

