A two-stage exon recognition model based on synergetic neural network
- PMID: 24790638
- PMCID: PMC3984832
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/503132
A two-stage exon recognition model based on synergetic neural network
Abstract
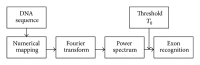
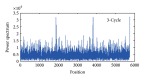
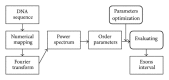
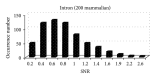
Exon recognition is a fundamental task in bioinformatics to identify the exons of DNA sequence. Currently, exon recognition algorithms based on digital signal processing techniques have been widely used. Unfortunately, these methods require many calculations, resulting in low recognition efficiency. In order to overcome this limitation, a two-stage exon recognition model is proposed and implemented in this paper. There are three main works. Firstly, we use synergetic neural network to rapidly determine initial exon intervals. Secondly, adaptive sliding window is used to accurately discriminate the final exon intervals. Finally, parameter optimization based on artificial fish swarm algorithm is used to determine different species thresholds and corresponding adjustment parameters of adaptive windows. Experimental results show that the proposed model has better performance for exon recognition and provides a practical solution and a promising future for other recognition tasks.
Figures





References
-
- Burge CB, Karlin S. Finding the genes in genomic DNA. Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 1998;8(3):346–354. - PubMed
-
- Sharma SD, Shakya K, Sharma SN. Evaluation of DNA mapping schemes for exon detection. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer, Communication and Electrical Technology (ICCCET '11); March 2011; pp. 71–74.
-
- Yin C, Yau SS-T. Prediction of protein coding regions by the 3-base periodicity analysis of a DNA sequence. Journal of Theoretical Biology. 2007;247(4):687–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

