The role of vitamin e in human health and some diseases
- PMID: 24790736
- PMCID: PMC3997530
The role of vitamin e in human health and some diseases
Abstract
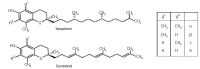
Vitamin E is the major lipid-soluble component in the cell antioxidant defence system and is exclusively obtained from the diet. It has numerous important roles within the body because of its antioxidant activity. Oxidation has been linked to numerous possible conditions and diseases, including cancer, ageing, arthritis and cataracts; vitamin E has been shown to be effective against these. Platelet hyperaggregation, which can lead to atherosclerosis, may also be prevented by vitamin E; additionally, it also helps to reduce the production of prostaglandins such as thromboxane, which cause platelet clumping. The current literature review discusses the functions and roles of vitamin E in human health and some diseases as well as the consequences of vitamin E deficiency. The main focus of the review is on the tocopherol class of the vitamers.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Health; Tocopherols; Vitamin E.
Figures

References
-
- Niki E, Traber MG. A history of vitamin E. Ann Nutr Metab. 2012;61:207–12. - PubMed
-
- Zingg JM. Vitamin E: An overview of major research directions. Mol Aspects Med. 2007;28:400–422. - PubMed
-
- Chow CK. Distribution of tocopherols in human plasma and red blood cells. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975;28:756–60. - PubMed
-
- Drotleff AM, Ternes W. Determination of RS,E/Z-tocotrienols by HPLC. J Chomatogr A. 2001;909:215–23. - PubMed
-
- Zingg JM. Molecular and cellular activities of vitamin E analogues. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007;7:543–58. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
