NFkB and Nrf2 in esophageal epithelial barrier function
- PMID: 24790804
- PMCID: PMC3943848
- DOI: 10.4161/tisb.27463
NFkB and Nrf2 in esophageal epithelial barrier function
Abstract
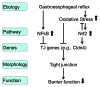
The stratified squamous epithelium of the esophagus forms a tight protective barrier. Defects of the barrier function contribute to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is manifested as damage to the esophageal epithelium due to exposure to the gastrointestinal refluxate. In this review, we discuss the involvement of NFkB and Nrf2 in esophageal epithelial barrier function. Understanding these molecular pathways in the esophagus may help us develop therapeutic strategies to improve clinical outcomes in patients with GERD.
Keywords: GERD; NFkB; Nrf2; esophageal barrier; esophageal epithelial barrier; esophageal epithelium; reflux disease; tight junction.
Figures
References
-
- Bateman DN, Colin-Jones D, Hartz S, Langman M, Logan RF, Mant J, Murphy M, Paterson KR, Rowsell R, Thomas S, et al. SURVEIL (Study of Undetected Reactions, Vigilance Enquiry into Links) Group Mortality study of 18 000 patients treated with omeprazole. Gut. 2003;52:942–6. doi: 10.1136/gut.52.7.942. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources