Factors influencing anti-asthmatic generic drug consumption in Morocco: 1999-2010
- PMID: 24790832
- PMCID: PMC4002999
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-192
Factors influencing anti-asthmatic generic drug consumption in Morocco: 1999-2010
Abstract
Background: The increasing availability of generic drugs (GD) resulted in a remarkable reduction in treatment costs that allowed a better access to health care.The aim of this study is to evaluate the share of anti-asthmatic generic drugs during the period 1999-2010 in Morocco and to look at the factors influencing generic development.
Methods: In this study, we used Moroccan sales data from IMS Health (Intercontinental Marketing Services). The consumption of the drugs was expressed in DDD/1000 inhabitants/day according to the WHO ATC/DDD methodology.
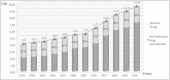
Results: Between 1999 and 2010, anti-asthmatic consumption increased from 3.91 to 14.43 DDD/1000 inhabitants/day. The market of anti-asthmatic generic drugs progressed from 1.83 (47%) to 2.18 (23%) DDD/1000 inhabitants/day from 1999 to 2010. In 2010, inhaled glucocorticosteroids ranked first (0.83 DDD/1000 inhabitants/day), followed by inhaled short acting beta agonists (0.73 DDD/1000 inhabitants/day). The number of brands went from 27 in 1999 to 34 in 2010, with a generic share increasing from 55.55% to 70.59%. The number of anti-asthmatic pharmaceutical preparations increased from 57 to 64 during the same period, of which 31 and 42 were generic preparations. In 2010, the total cost of anti-asthmatic dugs was about 22 million euro, the generics representing 14 million euro.
Conclusion: Despite the introduction of a compulsory insurance scheme called "AMO", that allows a refund for 69.5% of anti-asthmatic specialties marketed in Morocco, anti-asthmatic generic drug consumption remains limited. The Moroccan market is still largely dominated by the originator drugs with still valid patents.
Keywords: Antiasthmatics; Compulsory health insurance; Drug consumption; Generic drugs; Morocco; Originator drugs; Pricing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends in the use of antiasthmatic medications in Morocco (1999-2010).Springerplus. 2013 Dec;2(1):82. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-2-82. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Springerplus. 2013. PMID: 23519830 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in antihypertensives use among Moroccan patients.Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012 Oct;21(10):1067-73. doi: 10.1002/pds.3288. Epub 2012 May 14. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012. PMID: 22585420
-
[Generic drugs and the consumption trends of antihypertensives in Morocco].Therapie. 2013 Sep-Oct;68(5):303-12. doi: 10.2515/therapie/2013048. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Therapie. 2013. PMID: 24225041 French.
-
Impact of European pharmaceutical price regulation on generic price competition: a review.Pharmacoeconomics. 2010;28(8):649-63. doi: 10.2165/11535360-000000000-00000. Pharmacoeconomics. 2010. PMID: 20515079 Review.
-
Generics: keep a balanced view.Prescrire Int. 2014 Feb;23(146):52-5. Prescrire Int. 2014. PMID: 24669392 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors associated with asthma control: MOSAR study (Multicenter Observational Study of Asthma in Rabat-Morocco).BMC Pulm Med. 2018 Apr 24;18(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0624-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2018. PMID: 29699541 Free PMC article.
-
Costs associated with management of non-communicable diseases in the Arab Region: a scoping review.J Glob Health. 2018 Dec;8(2):020410. doi: 10.7189/jogh.08.020410. J Glob Health. 2018. PMID: 30546867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou-Atmé B, Lupien J, Bussières J-F, Daniel JGT. Pharmactuel 39 N°1. 2006. Applicabilité du système de classification anatomique, thérapeutique et chimique et dose définie journalière aux établissements de santé québécois pour mesurer l’utilisation des médica.
-
- Bilan de l’assurance maladie Oligatoire. 2011.
-
- Le secteur du médicament générique au Maroc. 2008.
-
- Le secteur pharmaceutique marocain: réalités sur le prix des médicaments et intérêt du secteur. 2010.
-
- Barnes PJ, Rodger IW, Neil Thomson C. Asthma. 3rd Edn: Basic mechanisms and clinical management. 1998.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials