Comparison of form-deprived myopia and lens-induced myopia in guinea pigs
- PMID: 24790865
- PMCID: PMC4003077
- DOI: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2014.02.10
Comparison of form-deprived myopia and lens-induced myopia in guinea pigs
Abstract
Aim: To study the efficacy difference between form-deprived myopia (FDM) and lens-induced myopia (LIM), the degree of myopia, axial length and pathological changes of the posterior sclera from guinea pigs were evaluated.
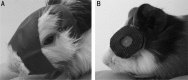
Methods: Four-week pigmented guinea pigs were randomly assigned into 3 groups, including normal control (n=6), FDM group with monocular cover (n=11) and LIM group with monocular -7D lens treatment (n=11). FDM group was form-deprived while LIM group was lens-induced for 14 d. Refractive error and axial length were measured prior to and post treatment, respectively. Morphological changes of sclera were examined using both light and electronic microscopes.
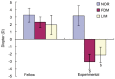
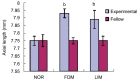
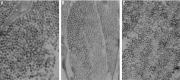
Results: After 14d treatment, refractive errors for FDM group and LIM group were -3.05±0.71D and -2.12±1.29D, respectively, which were significantly more myopic than that of normal controls and fellow control eyes (P<0.01). As for axial length, it was 7.93±0.03 mm for FDM group and 7.89±0.06 mm for LIM group, which were significantly longer than both normal and fellow controls (P<0.01). With respect to both refractory error and axial length, the differences between FDM group and LIM group were not significant (P>0.05). Under light microscope, both FDM group and LIM group showed thinned sclera, disarrangement of fibrosis and enlarged disassociation between fibers. Consistently, ultrastructural examination showed degenerated fibroblasts and thinned fibers in posterior sclera.
Conclusion: Following two weeks of myopia induction in guinea pigs, with regard to the degree of myopia, axial length and pathological alterations, there was no significant difference between FDM and LIM models. Therefore, FDM and LIM are equally effective and useful as a model of experimental myopia and guinea pigs are ideal animals for induction of experimental myopia because their high sensitivity to both form-deprivation and lens-induction.
Keywords: form-deprived myopia; lens-induced myopia; pathology.
Figures


References
-
- Edwards MH. Animal models of myopia: a review. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 1996;74(3):213–219. - PubMed
-
- Qian YS, Chu RY, Hu M, Hoffman MR. Sonic hedgehog expression and its role in form-deprivation myopia in mice. Curr Eye Res. 2009;34(8):623–635. - PubMed
-
- McFadden SA, Howlett MH, Mertz JR. Retinoic acid signals the direction of ocular elongation in the guinea pig eye. Vision Res. 2004;44(7):643–653. - PubMed
-
- Ashby RS, Megaw PL, Morgan IG. Changes in retinal alphaB-crystallin (cryab) RNA transcript levels during periods of altered ocular growth in chickens. Exp Eye Res. 2010;90(2):238–243. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
