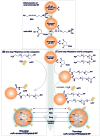
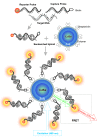
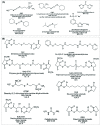
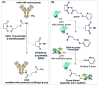
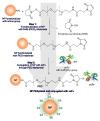
Surface modified multifunctional nanomedicines for simultaneous imaging and therapy of cancer
- PMID: 24790893
- PMCID: PMC4005281
- DOI: 10.5681/bi.2014.011
Surface modified multifunctional nanomedicines for simultaneous imaging and therapy of cancer
Abstract
Introduction: To date, a growing number of advanced anticancer nanomedicines (e.g., Doxil(®), Lipoxal(®), DepoCyte(®)) have entered into different phases of clinical trials. However, most of these medicaments fail to differentiate between diseased and normal cells. They also do not have capability of real time monitoring of disease status trough on-demand imaging/sensing of target molecule(s). Multifunctional nanomedicines and theranostics can resolve such limitations, while formulation of these advanced seamless systems appear to involve various sophisticated process, exploiting several bioconjugations.
Methods: Recent works upon multifunctional nanomedicines for simultaneous imaging and therapy of cancer have been systematically reviewed, focusing on surface modification and application of advanced nanobiomaterials.
Results: Ultimate therapy of malignancies, as complex systems, demands implementation of seamless nanosystems (NSs) that can specifically target the cancerous cells and smartly deliver the anticancer agent(s) into the desired target site. Engineering of such NSs requires in-situ coordination of various technologies (e.g., synthesis, surface modification and bioconjugation) in order to achieve improved pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics outcomes.
Conclusion: Seamless multimodal NSs have potential to simultaneously target and monitor the tumor cells through homing and imaging/sensing devices and deliver the therapeutic agents. However, to achieve superior pharmacokinetics with maximal efficacy and minimal side effects, these advanced NSs need to become much more intelligent to sense the disease condition and liberate therapeutics on demand.
Keywords: Cancer diagnosis; Cancer imaging; Cancer therapy; Nanomedicine; Theranostics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiolabeled theranostics: magnetic and gold nanoparticles.Bioimpacts. 2016;6(3):169-181. doi: 10.15171/bi.2016.23. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Bioimpacts. 2016. PMID: 27853680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent trends in targeted therapy of cancer using graphene oxide-modified multifunctional nanomedicines.J Drug Target. 2017 Mar;25(3):202-215. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2016.1238475. Epub 2016 Oct 6. J Drug Target. 2017. PMID: 27646598 Review.
-
Chitosan-based multifunctional nanomedicines and theranostics for targeted therapy of cancer.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):2110-2136. doi: 10.1002/med.21506. Epub 2018 May 30. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29846948 Review.
-
Impacts of quantum dots in molecular detection and bioimaging of cancer.Bioimpacts. 2014;4(3):149-66. doi: 10.15171/bi.2014.008. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Bioimpacts. 2014. PMID: 25337468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smart multifunctional theranostics: simultaneous diagnosis and therapy of cancer.Bioimpacts. 2011;1(3):145-7. doi: 10.5681/bi.2011.019. Epub 2011 Sep 30. Bioimpacts. 2011. PMID: 23678419 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles as Theranostic Vehicles in Experimental and Clinical Applications-Focus on Prostate and Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 May 20;18(5):1102. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051102. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28531102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FMSP-Nanoparticles Induced Cell Death on Human Breast Adenocarcinoma Cell Line (MCF-7 Cells): Morphometric Analysis.Biomolecules. 2018 May 23;8(2):32. doi: 10.3390/biom8020032. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 29882888 Free PMC article.
-
Radiolabeled theranostics: magnetic and gold nanoparticles.Bioimpacts. 2016;6(3):169-181. doi: 10.15171/bi.2016.23. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Bioimpacts. 2016. PMID: 27853680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Exploration of a Combination of Gambogic Acid with TiO₂ Nanofibers: The Photodynamic Effect for HepG2 Cell Proliferation.Materials (Basel). 2014 Sep 24;7(9):6865-6878. doi: 10.3390/ma7096865. Materials (Basel). 2014. PMID: 28788218 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic acid-modified theranostic niosomes for targeted Fingolimod delivery and inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 12;42(7):256. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02796-0. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40506644
References
-
- Cappellani A, Zanghi A, Di Vita M, Zanet E, Veroux P, Cacopardo B. et al. Clinical and biological markers in gastric cancer: update and perspectives. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2010;2:403–12. - PubMed
-
- Majidi J, Barar J, Baradaran B, Abdolalizadeh J, Omidi Y. Target therapy of cancer: implementation of monoclonal antibodies and nanobodies. Hum Antibodies. 2009;18:81–100. - PubMed
-
- Vafadar-Isfahani B, Laversin SA, Ahmad M, Ball G, Coveney C, Lemetre C. et al. Serum biomarkers which correlate with failure to respond to immunotherapy and tumor progression in a murine colorectal cancer model . Proteomics Clin Appl. 2010;4:682–96. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources