A comparison of the histological structure of the placenta in experimental animals
- PMID: 24791062
- PMCID: PMC4000068
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2013-0060
A comparison of the histological structure of the placenta in experimental animals
Erratum in
-
Errata (Printer's correction).J Toxicol Pathol. 2016 Jan;29(1):74. Epub 2016 Feb 17. J Toxicol Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26989306 Free PMC article.
Abstract
The primary function of the placenta is to act as an interface between the dam and fetus. The anatomic structure of the chorioallantoic placenta in eutherian mammals varies between different animal species. The placental types in eutherian mammals are classified from various standpoints based on the gross shape, the histological structure of the materno-fetal interface, the type of materno-fetal interdigitation, etc. Particularly, the histological structure is generally considered one of the most useful and instructive classifications for functionally describing placental type. In this system, three main types are recognized according to the cell layers comprising the interhemal area: (1) epitheliochorial type (horses, pigs and ruminants), (2) endotheliochorial type (carnivores) and (3) hemochorial type (primates, rodents and rabbits). The number of cell layers in the interhemal area is considered to modify the transfer of nutrients between maternal and fetal blood and is one of the important factors with respect to the difference in placental permeability between animal species. Therefore, in reproductive and developmental toxicity studies, careful attention should be paid to the histological structure of the interhemal area when extrapolating information concerning placental transfer characteristics to different animal species.
Keywords: cynomolgus monkey; dog; minipig; placenta; rabbit; rat.
Figures

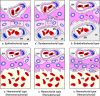
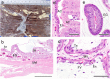


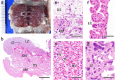
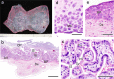
References
-
- Bauer MK, Harding JE, Bassett NS, Breier BH, Oliver MH, Gallaher BH, Evans PC, Woodall SM, and Gluckman PD. Fetal growth and placental function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 140: 115–120 1998. - PubMed
-
- Enders AC, and Blankenship TN. Comparative placental structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 38: 3–15 1999. - PubMed
-
- Ramsey EM. The placenta. Human and Animal. Praeger, New York. 1982
-
- Wooding P, and Burton G. Comparative Placentation. Structures, Functions and Evolution. Springer, Berlin. 2008
-
- Burton GJ, Kaufmann P, and Huppertz B. Anatomy and genesis of the Placenta. In: Knobil and Nell’s Physiology of Reproduction. 3rd ed. JD Neill (ed). Academic Press, Amsterdam. 189–243. 2006
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
