Study of extracellular matrix in vocal fold biomechanics using a two-phase model
- PMID: 24792897
- PMCID: PMC4218887
- DOI: 10.1007/s10237-014-0585-5
Study of extracellular matrix in vocal fold biomechanics using a two-phase model
Abstract
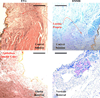
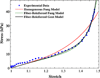
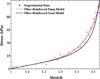
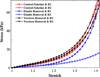
The extracellular matrix (ECM) of the vocal fold tissue consists primarily of fibrous and interstitial proteins. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of selective enzymatic digestion of two ECM proteins, namely elastin and versican, on the elasticity of rabbit vocal fold tissue. Quasi-static, sinusoidal, uniaxial tensile tests were performed. The data were analyzed within the framework of a model of the ECM as a two-phase composite material consisting of collagen fibrils as the reinforcing fibers and noncollagenous ECM proteins as the matrix. To validate the two-phase model, the regression parameters for the fibers' volume fraction and shear modulus in a different animal model were compared with corresponding published data. The proposed model was then used to analyze rabbit vocal fold tissues. The mean value and the standard deviation of the fiber volume fraction were found to be 8.49 ± 3.75 % for the control samples (n = 4), 0.59 ± 1.13 % after elastin removal (n = 4), and 8.22 ± 1.06 % after versican removal (n = 4). The results suggest that elastin removal may lead to a reduction in tissue stiffness, through counteracting the reinforcement of collagen fibrils.
Figures


References
-
- Agoras M, Lopez-Pamies O. A general hyperelastic model for incompressible fiber-reinforced elastomers. J Mech Phys Solids. 2009;57(2):268–286.
-
- Avazmohammadi R, Ponte Castañeda P. Tangent secondorder estimates for the large-strain, macroscopic response of particle-reinforced elastomers. J Elast. 2013;112(2):139–183.
-
- Avazmohammadi R, Naghdabadi R. Strain energy-based homogenization of nonlinear elastic particulate composites. Int J Eng Sci. 2009;47(10):1038–1048.
-
- Buhler RB, Sennes LU, Tsuji DH, Mauad T, Saldiva PN. Collagen type I, collagen type III, versican in vocal fold lamina propria. Arch Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2011;137(6):604–608. - PubMed
-
- DeBotton G. Transversely isotropic sequentially laminated composites in finite elasticity. J Mech Phys Solids. 2005;53(6):1334–1361.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

