Aberrant topoisomerase-1 DNA lesions are pathogenic in neurodegenerative genome instability syndromes
- PMID: 24793032
- PMCID: PMC4074009
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3715
Aberrant topoisomerase-1 DNA lesions are pathogenic in neurodegenerative genome instability syndromes
Abstract
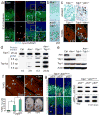
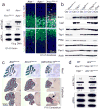
DNA damage is considered to be a prime factor in several spinocerebellar neurodegenerative diseases; however, the DNA lesions underpinning disease etiology are unknown. We observed the endogenous accumulation of pathogenic topoisomerase-1 (Top1)-DNA cleavage complexes (Top1ccs) in murine models of ataxia telangiectasia and spinocerebellar ataxia with axonal neuropathy 1. We found that the defective DNA damage response factors in these two diseases cooperatively modulated Top1cc turnover in a non-epistatic and ATM kinase-independent manner. Furthermore, coincident neural inactivation of ATM and DNA single-strand break repair factors, including tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase-1 or XRCC1, resulted in increased Top1cc formation and excessive DNA damage and neurodevelopmental defects. Notably, direct Top1 poisoning to elevate Top1cc levels phenocopied the neuropathology of the mouse models described above. Our results identify a critical endogenous pathogenic lesion associated with neurodegenerative syndromes arising from DNA repair deficiency, indicating that genome integrity is important for preventing disease in the nervous system.
Figures
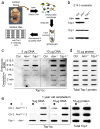
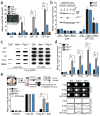
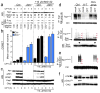
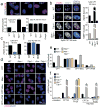
Similar articles
-
DNA-PK triggers histone ubiquitination and signaling in response to DNA double-strand breaks produced during the repair of transcription-blocking topoisomerase I lesions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Feb 18;44(3):1161-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1196. Epub 2015 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26578593 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary ataxia SCAN1 cells are defective for the repair of transcription-dependent topoisomerase I cleavage complexes.DNA Repair (Amst). 2006 Dec 9;5(12):1489-94. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2006.07.004. Epub 2006 Aug 28. DNA Repair (Amst). 2006. PMID: 16935573
-
SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase, Rad60, and Nse2 SUMO ligase suppress spontaneous Top1-mediated DNA damage and genome instability.PLoS Genet. 2011 Mar;7(3):e1001320. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001320. Epub 2011 Mar 3. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21408210 Free PMC article.
-
Abortive activity of Topoisomerase I: a challenge for genome integrity?Curr Genet. 2019 Oct;65(5):1141-1144. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00984-w. Epub 2019 May 2. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 31049660 Review.
-
The role of single strand break repair pathways in cellular responses to camptothecin induced DNA damage.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 May;125:109875. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109875. Epub 2020 Feb 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32036211 Review.
Cited by
-
Topoisomerases and the regulation of neural function.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016 Nov;17(11):673-679. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2016.101. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27630045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective repair of topoisomerase I induced chromosomal damage in Huntington's disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Feb 28;79(3):160. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04204-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35224690 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent DNA damage associated with ATM kinase deficiency promotes microglial dysfunction.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Mar 21;50(5):2700-2718. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac104. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35212385 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-PKcs, ATM, and ATR Interplay Maintains Genome Integrity during Neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2017 Jan 25;37(4):893-905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4213-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28123024 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Organization Drives Chromosome Fragility.Cell. 2017 Jul 27;170(3):507-521.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.06.034. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28735753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O’Driscoll M, Jeggo PA. The role of double-strand break repair - insights from human genetics. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:45–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R13 CA162528/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS037956/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA082313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52814/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA21765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA82313/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA096832/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052814/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-96832/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS037956/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM059413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-37956/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- GM59413/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

