Magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion biopsy for prediction of final prostate pathology
- PMID: 24793118
- PMCID: PMC4201866
- DOI: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.04.094
Magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion biopsy for prediction of final prostate pathology
Abstract
Purpose: We explored the impact of magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy on the prediction of final surgical pathology.
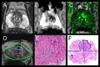
Materials and methods: A total of 54 consecutive men undergoing radical prostatectomy at UCLA after fusion biopsy were included in this prospective, institutional review board approved pilot study. Using magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion, tissue was obtained from a 12-point systematic grid (mapping biopsy) and from regions of interest detected by multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (targeted biopsy). A single radiologist read all magnetic resonance imaging, and a single pathologist independently rereviewed all biopsy and whole mount pathology, blinded to prior interpretation and matched specimen. Gleason score concordance between biopsy and prostatectomy was the primary end point.
Results: Mean patient age was 62 years and median prostate specific antigen was 6.2 ng/ml. Final Gleason score at prostatectomy was 6 (13%), 7 (70%) and 8-9 (17%). A tertiary pattern was detected in 17 (31%) men. Of 45 high suspicion (image grade 4-5) magnetic resonance imaging targets 32 (71%) contained prostate cancer. The per core cancer detection rate was 20% by systematic mapping biopsy and 42% by targeted biopsy. The highest Gleason pattern at prostatectomy was detected by systematic mapping biopsy in 54%, targeted biopsy in 54% and a combination in 81% of cases. Overall 17% of cases were upgraded from fusion biopsy to final pathology and 1 (2%) was downgraded. The combination of targeted biopsy and systematic mapping biopsy was needed to obtain the best predictive accuracy.
Conclusions: In this pilot study magnetic resonance imaging-ultrasound fusion biopsy allowed for the prediction of final prostate pathology with greater accuracy than that reported previously using conventional methods (81% vs 40% to 65%). If confirmed, these results will have important clinical implications.
Keywords: biopsy; magnetic resonance imaging; prostatectomy; prostatic neoplasms; ultrasonography.
Copyright © 2014 American Urological Association Education and Research, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
FINANCIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: None
Figures
References
-
- King CR, Long JP. Prostate biopsy grading errors: a sampling problem? Int J Cancer. 2000;90:326–330. - PubMed
-
- Cohen MS, Hanley RS, Kurteva T, et al. Comparing the Gleason prostate biopsy and Gleason prostatectomy grading system: the Lahey Clinic Medical Center experience and an international meta-analysis. Eur Urol. 2008;54:371–381. - PubMed
-
- D'Amico AV, Whittington R, Malkowicz SB, et al. Biochemical outcome after radical prostatectomy, external beam radiation therapy, or interstitial radiation therapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. JAMA. 1998;280:969–974. - PubMed
-
- Kattan MW, Wheeler TM, Scardino PT. Postoperative nomogram for disease recurrence after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:1499–1507. - PubMed
-
- Sved PD, Gomez P, Manoharan M, et al. Limitations of biopsy Gleason grade: implications for counseling patients with biopsy Gleason score 6 prostate cancer. J Urol. 2004;172:98–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

