Atorvastatin prevents amyloid-β peptide oligomer-induced synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction in rats through a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway
- PMID: 24793311
- PMCID: PMC4086387
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2013.203
Atorvastatin prevents amyloid-β peptide oligomer-induced synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction in rats through a p38 MAPK-dependent pathway
Abstract
Aim: To investigate whether atorvastatin treatment could prevent Aβ1-42 oligomer (AβO)-induced synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction in rats, and to elucidate the mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective actions of atorvastatin.
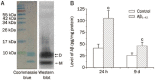
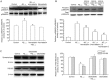
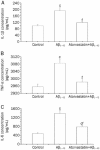
Methods: SD rats were injected with AβOs (5 nmol, icv). The rats were administrated with atorvastatin (10 mg·kg(-1)·d(-1), po) for 2 consecutive weeks (the first dose was given 5 d before AβOs injection). The memory impairments were evaluated with Morris water maze task. The expression of inflammatory cytokines in the hippocampus was determined using ELISA assays. The levels of PSD-95 and p38MAPK proteins in rat hippocampus were evaluated using Western blot analysis. For in vitro experiments, cultured rat hippocampal neurons were treated with AβOs (50 nmol/L) for 48 h. The expression of MAP-2 and synaptophysin in the neurons was detected with immunofluorescence.
Results: The AβO-treated rats displayed severe memory impairments in Morris water maze tests, and markedly reduced levels of synaptic proteins synaptophysin and PSD-95, increased levels of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α) and p38MAPK activation in the hippocampus. All these effects were prevented or substantially attenuated by atorvastatin administration. Pretreatment of cultured hippocampal neurons with atorvastatin (1 and 5 μmol/L) concentration-dependently attenuated the AβO-induced synaptotoxicity, including the loss of dendritic marker MAP-2, and synaptic proteins synaptophysin and PSD-95. Pretreatment of the cultured hippocampal neurons with the p38MAPK inhibitor SB203580 (5 μmol/L) blocked the AβO-induced loss of synaptophysin and PSD-95.
Conclusion: Atorvastatin prevents AβO-induced synaptotoxicity and memory dysfunction through a p38MAPK-dependent pathway.
Figures




References
-
- Haass C, Selkoe DJ. Soluble protein oligomers in neurodegeneration: lessons from the Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:101–12. - PubMed
-
- Cerpa W, Dinamarca MC, Inestrosa NC. Structure–function implications in Alzheimer's disease: effect of Abeta oligomers at central synapses. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008;5:233–43. - PubMed
-
- Chang L, Bakhos L, Wang Z, Venton DL, Klein WL. Femtomole immunodetection of synthetic and endogenous amyloid-beta oligomers and its application to Alzheimer's disease drug candidate screening. J Mol Neurosci. 2003;20:305–13. - PubMed
-
- Cleary JP, Walsh DM, Hofmeister JJ, Shankar GM, Kuskowski MA, Selkoe DJ, et al. Natural oligomers of the amyloid-beta protein specifically disrupt cognitive function. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:79–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

