Telmisartan protects central neurons against nutrient deprivation-induced apoptosis in vitro through activation of PPARγ and the Akt/GSK-3β pathway
- PMID: 24793312
- PMCID: PMC4086392
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2013.199
Telmisartan protects central neurons against nutrient deprivation-induced apoptosis in vitro through activation of PPARγ and the Akt/GSK-3β pathway
Abstract
Aim: To determine whether angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) could protect central neurons against nutrient deprivation-induced apoptosis in vitro and to elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
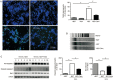
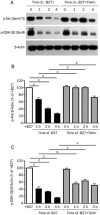
Methods: Primary rat cerebellar granule cells (CGCs) underwent B27 (a serum substitute) deprivation for 24 h to induce neurotoxicity, and cell viability was analyzed using LDH assay and WST-1 assay. DNA laddering assay and TUNEL assay were used to detect cell apoptosis. The expression of caspase-3 and Bcl-2, and the phosphorylation of Akt and GSK-3β were detected using Western blot analysis. AT1a mRNA expression was determined using RT-PCR analysis.
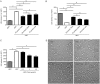
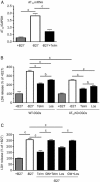
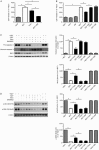
Results: B27 deprivation significantly increased the apoptosis of CGCs, as demonstrated by LDH release, DNA laddering, caspase-3 activation and positive TUNEL staining. Pretreatment with 10 μmol/L ARBs (telmisartan, candesartan or losartan) partially blocked B27 deprivation-induced apoptosis of CGCs with telmisartan being the most effective one. B27 deprivation markedly increased the expression of AT1a receptor in CGCs, inhibited Akt and GSK-3β activation, decreased Bcl-2 level, and activated caspase-3, which were reversed by pretreatment with 1 μmol/L telmisartan. In addition, pretreatment with 10 μmol/L PPARγ agonist pioglitazone was more effective in protecting CGCs against B27 deprivation-induced apoptosis, whereas pretreatment with 20 μmol/L PPARγ antagonist GW9662 abolished all the effects of telmisartan in CGCs deprived of B27.
Conclusion: ARBs, in particular telmisartan, can protect the nutrient deprivation-induced apoptosis of CGCs in vitro through activation of PPARγ and the Akt/GSK-3β pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Telmisartan ameliorates glutamate-induced neurotoxicity: roles of AT(1) receptor blockade and PPARγ activation.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:249-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.022. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24316465 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery endothelial dysfunction through a PPAR gamma-dependent PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Jun;28(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2013.11.003. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24269521
-
Telmisartan-induced inhibition of vascular cell proliferation beyond angiotensin receptor blockade and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation.Hypertension. 2009 Dec;54(6):1353-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.138750. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Hypertension. 2009. PMID: 19822796 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan directly ameliorates the neuronal inflammatory response to IL-1β partly through the JNK/c-Jun and NADPH oxidase pathways.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 May 29;9:102. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-102. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22642771 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and ERK1/2 pathways mediate protective effects of acylated and unacylated ghrelin against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced apoptosis in primary rat cortical neuronal cells.J Endocrinol. 2008 Sep;198(3):511-21. doi: 10.1677/JOE-08-0160. Epub 2008 Jun 9. J Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18541646
Cited by
-
Ciliogenesis is Not Directly Regulated by LRRK2 Kinase Activity in Neurons.Exp Neurobiol. 2021 Jun 30;30(3):232-243. doi: 10.5607/en21003. Exp Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34230223 Free PMC article.
-
[Activation of PPARγ pathway enhances cellular anti-oxidant capacity to protect long-term cultured primary rat neural cells from apoptosis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Jan 30;39(1):23-29. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.01.04. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 30692062 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Addressing Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma in 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Neurotoxicity in Rats.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jul;59(7):4368-4383. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02856-w. Epub 2022 May 12. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35553009 Free PMC article.
-
The natural product 4,10-aromadendranediol induces neuritogenesis in neuronal cells in vitro through activation of the ERK pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017 Jan;38(1):29-40. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.115. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017. PMID: 27840407 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma on milk fat synthesis in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016 Dec;52(10):1044-1059. doi: 10.1007/s11626-016-0059-4. Epub 2016 Jun 10. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2016. PMID: 27287918
References
-
- Dzau VJ, Ingelfinger J, Pratt RE, Ellison KE. Identification of renin and angiotensinogen messenger RNA sequences in mouse and rat brains. Hypertension. 1986;8:544–8. - PubMed
-
- Gyurko R, Wielbo D, Phillips MI. Antisense inhibition of AT1 receptor mRNA and angiotensinogen mRNA in the brain of spontaneously hypertensive rats reduces hypertension of neurogenic origin. Regul Pept. 1993;49:167–74. - PubMed
-
- Inaba S, Iwai M, Tomono Y, Senba I, Furuno M, Kanno H, et al. Exaggeration of focal cerebral ischemia in transgenic mice carrying human renin and human angiotensinogen genes. Stroke. 2008;40:597–603. - PubMed
-
- AbdAlla S, Lother H, el Missiry A, Langer A, Sergeev P, el Faramawy, et al. Angiotensin II AT2 receptor oligomers mediate G-protein dysfunction in an animal model of Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:6554–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

