Effects of oral exposure to naturally-occurring and synthetic deoxynivalenol congeners on proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA expression in the mouse
- PMID: 24793808
- PMCID: PMC4408533
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.04.016
Effects of oral exposure to naturally-occurring and synthetic deoxynivalenol congeners on proinflammatory cytokine and chemokine mRNA expression in the mouse
Abstract
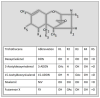
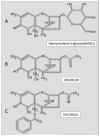
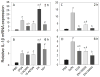
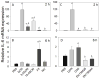
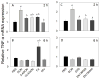
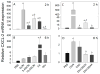
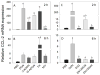
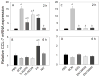
The foodborne mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) induces a ribotoxic stress response in mononuclear phagocytes that mediate aberrant multi-organ upregulation of TNF-α, interleukins and chemokines in experimental animals. While other DON congeners also exist as food contaminants or pharmacologically-active derivatives, it is not known how these compounds affect expression of these cytokine genes in vivo. To address this gap, we compared in mice the acute effects of oral DON exposure to that of seven relevant congeners on splenic expression of representative cytokine mRNAs after 2 and 6h. Congeners included the 8-ketotrichothecenes 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol (3-ADON), 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol (15-ADON), fusarenon X (FX), nivalenol (NIV), the plant metabolite DON-3-glucoside (D3G) and two synthetic DON derivatives with novel satiety-inducing properties (EN139528 and EN139544). DON markedly induced transient upregulation of TNF-α IL-1β, IL-6, CXCL-2, CCL-2 and CCL-7 mRNA expressions. The two ADONs also evoked mRNA expression of these genes but to a relatively lesser extent. FX induced more persistent responses than the other DON congeners and, compared to DON, was: 1) more potent in inducing IL-1β mRNA, 2) approximately equipotent in the induction of TNF-α and CCL-2 mRNAs, and 3) less potent at upregulating IL-6, CXCL-2, and CCL-2 mRNAs. EN139528's effects were similar to NIV, the least potent 8-ketotrichothecene, while D3G and EN139544 were largely incapable of eliciting cytokine or chemokine mRNA responses. Taken together, the results presented herein provide important new insights into the potential of naturally-occurring and synthetic DON congeners to elicit aberrant mRNA upregulation of cytokines associated with acute and chronic trichothecene toxicity.
Keywords: 8-Ketotrichothecenes; Chemokine; Cytokine; Deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside; EN139528; EN139544.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An overview of the toxicology and toxicokinetics of fusarenon-X, a type B trichothecene mycotoxin.J Vet Med Sci. 2017 Jan 20;79(1):6-13. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0008. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Vet Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27534911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of anorectic and emetic potencies of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin) to the plant metabolite deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside and synthetic deoxynivalenol derivatives EN139528 and EN139544.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Nov;142(1):167-81. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu166. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25173790 Free PMC article.
-
Role of cholecystokinin in anorexia induction following oral exposure to the 8-ketotrichothecenes deoxynivalenol, 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol, 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol, fusarenon X, and nivalenol.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Apr;138(2):278-89. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft335. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24385417 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of murine anorectic responses to the 8-ketotrichothecenes 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol, 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol, fusarenon X and nivalenol.Food Chem Toxicol. 2012 Jun;50(6):2056-61. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.03.055. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Food Chem Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22465835
-
Deoxynivalenol-induced proinflammatory gene expression: mechanisms and pathological sequelae.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Jun;2(6):1300-17. doi: 10.3390/toxins2061300. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Risks to human and animal health related to the presence of deoxynivalenol and its acetylated and modified forms in food and feed.EFSA J. 2017 Sep 11;15(9):e04718. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4718. eCollection 2017 Sep. EFSA J. 2017. PMID: 32625635 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Effect of Deoxynivalenol (DON) and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 (Pcv2) on Inflammatory Cytokine mRNA Expression.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jun 13;13(6):422. doi: 10.3390/toxins13060422. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34199278 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of biological feed additives on gut microbiota and the health of pigs exposed to deoxynivalenol: a review.J Anim Sci Technol. 2022 Jul;64(4):640-653. doi: 10.5187/jast.2022.e40. Epub 2022 Jul 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35969702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestinal toxicity of the type B trichothecene mycotoxin fusarenon-X: whole transcriptome profiling reveals new signaling pathways.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 8;7(1):7530. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07155-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28790326 Free PMC article.
-
An overview of the toxicology and toxicokinetics of fusarenon-X, a type B trichothecene mycotoxin.J Vet Med Sci. 2017 Jan 20;79(1):6-13. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0008. Epub 2016 Aug 18. J Vet Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27534911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amuzie CJ, Harkema JR, Pestka JJ. Tissue distribution and proinflammatory cytokine induction by the trichothecene deoxynivalenol in the mouse: comparison of nasal vs. oral exposure. Toxicol. 2008;248:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Azcona-Olivera JI, Ouyang Y, Murtha J, Chu FS, Pestka JJ. Induction of cytokine mRNAs in mice after oral exposure to the trichothecene vomitoxin (deoxynivalenol): relationship to toxin distribution and protein synthesis inhibition. Toxicol. Appl Pharmacol. 1995;133:109–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

