2014 global geographic analysis of mortality from ischaemic heart disease by country, age and income: statistics from World Health Organisation and United Nations
- PMID: 24794549
- PMCID: PMC4045191
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.04.096
2014 global geographic analysis of mortality from ischaemic heart disease by country, age and income: statistics from World Health Organisation and United Nations
Abstract
Background: Ischaemic heart disease (IHD) is the leading cause of death worldwide and its prevention is a public health priority.
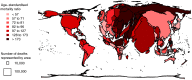
Method: We analysed worldwide IHD mortality data from the World Health Organisation as of February 2014 by country, age and income. Age-standardised mortality rates by country were calculated. We constructed a cartogram which is an algorithmically transformed world map that conveys numbers of deaths in the form of spatial area.
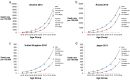
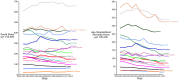
Results: Of the countries that provided mortality data, Russia, the United States of America and Ukraine contributed the largest numbers of deaths. India and China were estimated to have even larger numbers of deaths. Death rates from IHD increase rapidly with age. Crude mortality rates appear to be stable whilst age-standardised mortality rates are falling. Over half of the world's countries (113/216) have provided IHD mortality data for 2008 or later. Of these, 13 countries provided data in 2012. No countries have yet provided 2013 data. Of the 103 remaining countries, 24 provided data in 2007 or earlier, and 79 have never provided data in the ICD9 or ICD10 format.
Conclusions: In the countries for which there are good longitudinal data, predominantly European countries, recent years have shown a continuing decline in age-standardised IHD mortality. However, the progressive aging of populations has kept crude IHD mortality high. It is not known whether the pattern is consistent globally because many countries have not provided regular annual data including wealthy countries such as the United Arab Emirates and large countries such as India and China.
Keywords: Cartogram; Coronary heart disease; Ischaemic heart disease; Mortality.
Copyright © 2014. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- WHO; 2013. WHO | The top 10 causes of death. [Internet] (accessed on 30 Mar 2014 available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/)
-
- Danny Dorling; 1996. Area cartograms: their use and creation. [Internet] (accessed on 30 Mar 2014 available from: http://www.dannydorling.org/?page_id=1448)
-
- WHO; 2011. WHO | Information on estimation methods. [Internet] (accessed on 30 Mar 2014 available from: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/methods/en/)
-
- United Nations; 2002. Methods for estimating adult mortality. [Internet] (accessed on 30 Mar 2014 available from: http://www.un.org/esa/population/techcoop/DemEst/methods_adultmort/metho...)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

