Eph- and ephrin-dependent mechanisms in tumor and stem cell dynamics
- PMID: 24794629
- PMCID: PMC11113620
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-014-1633-0
Eph- and ephrin-dependent mechanisms in tumor and stem cell dynamics
Abstract
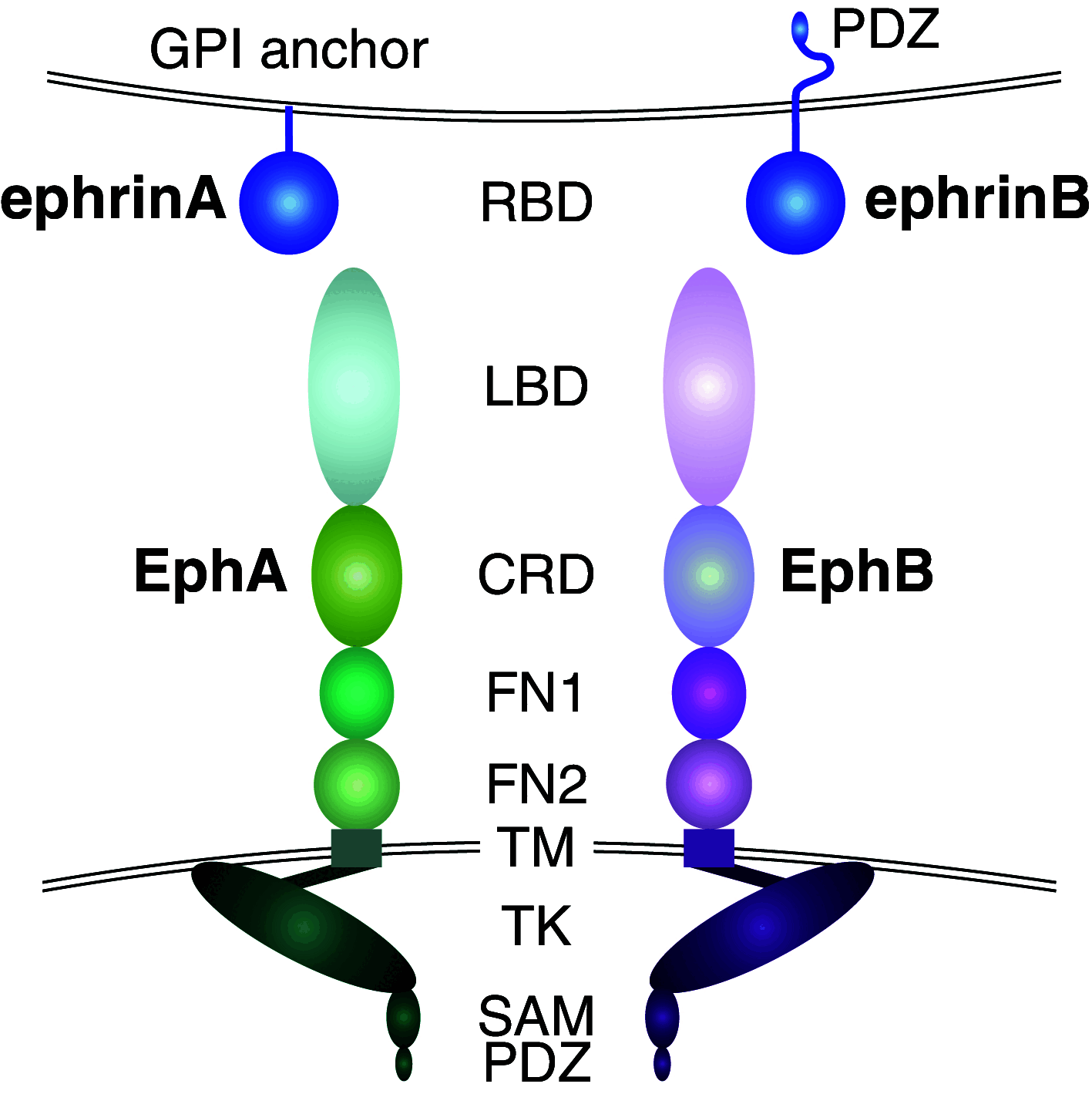
The erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular (Eph) receptors comprise the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Initially regarded as axon-guidance and tissue-patterning molecules, Eph receptors have now been attributed with various functions during development, tissue homeostasis, and disease pathogenesis. Their ligands, ephrins, are synthesized as membrane-associated molecules. At least two properties make this signaling system unique: (1) the signal can be simultaneously transduced in the receptor- and the ligand-expressing cell, (2) the signaling outcome through the same molecules can be opposite depending on cellular context. Moreover, shedding of Eph and ephrin ectodomains as well as ligand-dependent and -independent receptor crosstalk with other RTKs, proteases, and adhesion molecules broadens the repertoire of Eph/ephrin functions. These integrated pathways provide plasticity to cell-microenvironment communication in varying tissue contexts. The complex molecular networks and dynamic cellular outcomes connected to the Eph/ephrin signaling in tumor-host communication and stem cell niche are the main focus of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eph receptor and ephrin function in breast, gut, and skin epithelia.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(4):327-38. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.970012. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 25482622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in cancer stem cells.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015 Feb;26(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 May 17. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. PMID: 24933439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eph/ephrin signaling in morphogenesis, neural development and plasticity.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;16(5):580-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2004.07.002. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15363810 Review.
-
Eph/ephrin signaling in cancer: intricate, puzzling and ... fascinating!Cell Adh Migr. 2012 Mar-Apr;6(2):100-1. doi: 10.4161/cam.20890. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2012. PMID: 22814609 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004 Dec;15(6):419-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2004.09.002. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004. PMID: 15561600 Review.
Cited by
-
ProNGF promotes brain metastasis through TrkA/EphA2 induced Src activation in triple negative breast cancer cells.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023 Dec 10;12(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00463-6. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38072918 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory System for Stem/Progenitor Cell Niches in the Adult Rodent Pituitary.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 9;17(1):75. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010075. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26761002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The putative tumor suppressor gene EphA7 is a novel BMI-1 target.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58203-58217. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11279. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27533460 Free PMC article.
-
Eph receptor and ephrin function in breast, gut, and skin epithelia.Cell Adh Migr. 2014;8(4):327-38. doi: 10.4161/19336918.2014.970012. Cell Adh Migr. 2014. PMID: 25482622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ephrin-A4 Ligand (EFNA4) Predicts Poor Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Promotes Tumor Proliferation.J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023 Sep-Oct;13(5):767-773. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2023.04.004. Epub 2023 Apr 15. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37693261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J, Takaku F. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science. 1987;238:1717–1720. - PubMed
-
- Pasquale EB. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 2008;133:38–52. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson DG. Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:155–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

