Transcriptional coregulators: fine-tuning metabolism
- PMID: 24794975
- PMCID: PMC4079747
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.03.027
Transcriptional coregulators: fine-tuning metabolism
Abstract
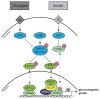
Metabolic homeostasis requires that cellular energy levels are adapted to environmental cues. This adaptation is largely regulated at the transcriptional level, through the interaction between transcription factors, coregulators, and the basal transcriptional machinery. Coregulators, which function as both metabolic sensors and transcriptional effectors, are ideally positioned to synchronize metabolic pathways to environmental stimuli. The balance between inhibitory actions of corepressors and stimulatory effects of coactivators enables the fine-tuning of metabolic processes. This tight regulation opens therapeutic opportunities to manage metabolic dysfunction by directing the activity of cofactors toward specific transcription factors, pathways, or cells/tissues, thereby restoring whole-body metabolic homeostasis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Nuclear receptor coregulators as a new paradigm for therapeutic targeting.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Oct 30;62(13):1227-37. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.09.016. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010. PMID: 20933027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional coregulators in the control of energy homeostasis.Trends Cell Biol. 2007 Jun;17(6):292-301. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.04.001. Epub 2007 May 1. Trends Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17475497 Review.
-
Minireview: nuclear receptor coregulators of the p160 family: insights into inflammation and metabolism.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Apr;29(4):502-17. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1005. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25647480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptor coactivators: structural and functional biochemistry.Biochemistry. 2011 Jan 25;50(3):313-28. doi: 10.1021/bi101762x. Epub 2010 Dec 29. Biochemistry. 2011. PMID: 21141906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coregulator-mediated control of skeletal muscle plasticity - A mini-review.Biochimie. 2017 May;136:49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2016.12.011. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Biochimie. 2017. PMID: 28057584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Pdx1-Bound Swi/Snf Chromatin Remodeling Complex Regulates Pancreatic Progenitor Cell Proliferation and Mature Islet β-Cell Function.Diabetes. 2019 Sep;68(9):1806-1818. doi: 10.2337/db19-0349. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 31201281 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic sensor governing bacterial virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Nov 18;111(46):E4981-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411077111. Epub 2014 Nov 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25368190 Free PMC article.
-
Mitonuclear communication in homeostasis and stress.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Apr;17(4):213-26. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.23. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26956194 Review.
-
Proteome-wide analysis reveals widespread lysine acetylation of major protein complexes in the malaria parasite.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 27;6:19722. doi: 10.1038/srep19722. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26813983 Free PMC article.
-
The metabolic co-regulator PGC1α suppresses prostate cancer metastasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;18(6):645-656. doi: 10.1038/ncb3357. Epub 2016 May 23. Nat Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27214280 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astapova I, Vella KR, Ramadoss P, Holtz KA, Rodwin BA, Liao XH, Weiss RE, Rosenberg MA, Rosenzweig A, Hollenberg AN. The nuclear receptor corepressor (NCoR) controls thyroid hormone sensitivity and the set point of the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:212–224. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

