Multifunctional polymeric micelles for delivery of drugs and siRNA
- PMID: 24795633
- PMCID: PMC4007015
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00077
Multifunctional polymeric micelles for delivery of drugs and siRNA
Abstract
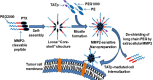
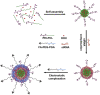
Polymeric micelles, self-assembling nano-constructs of amphiphilic copolymers with a core-shell structure have been used as versatile carriers for delivery of drugs as well as nucleic acids. They have gained immense popularity owing to a host of favorable properties including their capacity to effectively solubilize a variety of poorly soluble pharmaceutical agents, biocompatibility, longevity, high stability in vitro and in vivo and the ability to accumulate in pathological areas with compromised vasculature. Moreover, additional functions can be imparted to these micelles by engineering their surface with various ligands and cell-penetrating moieties to allow for specific targeting and intracellular accumulation, respectively, to load them with contrast agents to confer imaging capabilities, and incorporating stimuli-sensitive groups that allow drug release in response to small changes in the environment. Recently, there has been an increasing trend toward designing polymeric micelles which integrate a number of the above functions into a single carrier to give rise to "smart," multifunctional polymeric micelles. Such multifunctional micelles can be envisaged as key to improving the efficacy of current treatments which have seen a steady increase not only in hydrophobic small molecules, but also in biologics including therapeutic genes, antibodies and small interfering RNA (siRNA). The purpose of this review is to highlight recent advances in the development of multifunctional polymeric micelles specifically for delivery of drugs and siRNA. In spite of the tremendous potential of siRNA, its translation into clinics has been a significant challenge because of physiological barriers to its effective delivery and the lack of safe, effective and clinically suitable vehicles. To that end, we also discuss the potential and suitability of multifunctional polymeric micelles, including lipid-based micelles, as promising vehicles for both siRNA and drugs.
Keywords: micelles; multifunctional; nanocarriers; polymeric; siRNA; targeted.
Figures








References
-
- Abouzeid A. H., Patel N. R., Torchilin V. P. (2014). Polyethylene glycol-phosphatidylethanolamine (PEG-PE)/vitamin E micelles for co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin to overcome multi-drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 464, 178–184 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.01.009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

