The role of ubiquitin and the 26S proteasome in plant abiotic stress signaling
- PMID: 24795732
- PMCID: PMC3997020
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00135
The role of ubiquitin and the 26S proteasome in plant abiotic stress signaling
Abstract
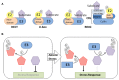
Ubiquitin is a small, highly conserved, ubiquitously expressed eukaryotic protein with immensely important and diverse regulatory functions. A well-studied function of ubiquitin is its role in selective proteolysis by the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS). The UPS has emerged as an integral player in plant response and adaptation to environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, cold and nutrient deprivation. The UPS has also been shown to influence the production and signal transduction of stress-related hormones such as abscisic acid. Understanding UPS function has centered mainly on defining the role of E3 ubiquitin ligases, which are the substrate-recruiting component of the ubiquitination pathway. The recent identification of stress signaling/regulatory proteins that are the subject of ubiquitin-dependent degradation has increased our knowledge of how the UPS facilitates responses to adverse environmental conditions. A brief overview is provided on role of the UPS in modulating protein stability during abiotic stress signaling. E3 ubiquitin ligases for which stress-related substrate proteins have been identified are discussed.
Keywords: 26S proteasome; E3 ubiquitin ligase; abiotic stress; abscisic acid; protein degradation; ubiquitination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in the plant response to abiotic stress: Potential role in crop resilience improvement.Plant Sci. 2024 May;342:112035. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112035. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38367822 Review.
-
Role of the Ubiquitin Proteasome System in Plant Response to Abiotic Stress.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019;343:65-110. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2018.05.012. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30712675 Review.
-
Arabidopsis RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase XBAT35.2 promotes proteasome-dependent degradation of ACD11 to attenuate abiotic stress tolerance.Plant J. 2020 Dec;104(6):1712-1723. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15032. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Plant J. 2020. PMID: 33080095
-
A review on ubiquitin ligases: Orchestrators of plant resilience in adversity.Plant Sci. 2024 Oct;347:112180. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112180. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38964613 Review.
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in plant responses to environments.Plant Cell Environ. 2019 Oct;42(10):2931-2944. doi: 10.1111/pce.13633. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Plant Cell Environ. 2019. PMID: 31364170 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome and Proteome Co-Profiling Offers an Understanding of Pre-Harvest Sprouting (PHS) Molecular Mechanisms in Wheat (Triticum aestivum).Plants (Basel). 2022 Oct 22;11(21):2807. doi: 10.3390/plants11212807. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36365261 Free PMC article.
-
Stress-Inducible Expression of an F-box Gene TaFBA1 from Wheat Enhanced the Drought Tolerance in Transgenic Tobacco Plants without Impacting Growth and Development.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Sep 5;7:1295. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01295. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27656187 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis uncovers different heat stress responses in heat-resistant and heat-sensitive jujube cultivars.PLoS One. 2020 Sep 21;15(9):e0235763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235763. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32956359 Free PMC article.
-
Codominant grasses differ in gene expression under experimental climate extremes in native tallgrass prairie.PeerJ. 2018 Feb 14;6:e4394. doi: 10.7717/peerj.4394. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 29473008 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and quantitative proteomic analyses unraveling potassium deficiency stress response in alligator weed (Alternanthera philoxeroides L.) root.Plant Mol Biol. 2018 Jun;97(3):265-278. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0738-5. Epub 2018 May 18. Plant Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29777486
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

