PET brain kinetics studies of (11)C-ITMM and (11)C-ITDM,radioprobes for metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1, in a nonhuman primate
- PMID: 24795840
- PMCID: PMC3999406
PET brain kinetics studies of (11)C-ITMM and (11)C-ITDM,radioprobes for metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1, in a nonhuman primate
Abstract
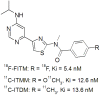
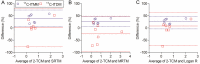
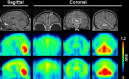
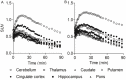
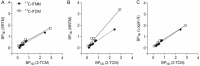
The metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (mGluR1) is a novel target protein for the development of new drugs against central nervous system disorders. Recently, we have developed (11)C-labeled PET probes (11)C-ITMM and (11)C-ITDM, which demonstrate similar profiles, for imaging of mGluR1. In the present study, we compared (11)C-ITMM and (11)C-ITDM PET imaging and quantitative analysis in the monkey brain. Respective PET images showed similar distribution of uptake in the cerebellum, thalamus, and cingulate cortex. Slightly higher uptake was detected with (11)C-ITDM than with (11)C-ITMM. For the kinetic analysis using the two-tissue compartment model (2-TCM), the distribution volume (VT) in the cerebellum, an mGluR1-rich region in the brain, was 2.5 mL∙cm(-3) for (11)C-ITMM and 3.6 mL∙cm(-3) for (11)C-ITDM. By contrast, the VT in the pons, a region with negligible mGluR1 expression, was similarly low for both radiopharmaceuticals. Based on these results, we performed noninvasive PET quantitative analysis with general reference tissue models using the time-activity curve of the pons as a reference region. We confirmed the relationship and differences between the reference tissue models and 2-TCM using correlational scatter plots and Bland-Altman plots analyses. Although the scattergrams of both radiopharmaceuticals showed over- or underestimations of reference tissue model-based the binding potentials against 2-TCM, there were no significant differences between the two kinetic analysis models. In conclusion, we first demonstrated the potentials of (11)C-ITMM and (11)C-ITDM for noninvasive PET quantitative analysis using reference tissue models. In addition, our findings suggest that (11)C-ITDM may be superior to (11)C-ITMM as a PET probe for imaging of mGluR1, because regional VT values in PET with (11)C-ITDM were higher than those of (11)C-ITMM. Clinical studies of (11)C-ITDM in humans will be necessary in the future.
Keywords: Central nervous system (CNS); metabotropic glutamate receptor type 1 (mGluR1); positron emission tomography (PET).
Figures

References
-
- Ferraguti F, Crepaldi L, Nicoletti F. Metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor: current concepts and perspectives. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:536–581. - PubMed
-
- Aramori I, Nakanishi S. Signal transduction and pharmacological characteristics of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR1, in transfected CHO cells. Neuron. 1992;8:757–765. - PubMed
-
- Di Matteo V, De Blasi A, Di Giulio C, Esposito E. Role of 5-HT(2C) receptors in the control of central dopamine function. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:229–232. - PubMed
-
- Francesconi A, Duvoisin RM. Role of the second and third intracellular loops of metabotropic glutamate receptors in mediating dual signal transduction activation. J Biol Chem. 1998;2731:5615–5624. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
