Supra-organismal interactions in the human intestine
- PMID: 24795867
- PMCID: PMC4005949
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00047
Supra-organismal interactions in the human intestine
Keywords: GI tract; dysbiosis; microbiome; supraorganism; virome.
Figures
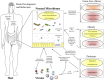
References
-
- Ayala F. J., Campbell C. A. (1974). Frequency-dependent selection. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 5, 115–138 10.1146/annurev.es.05.110174.000555 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

