Recombinant nAG (a salamander-derived protein) decreases the formation of hypertrophic scarring in the rabbit ear model
- PMID: 24795877
- PMCID: PMC3985163
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/121098
Recombinant nAG (a salamander-derived protein) decreases the formation of hypertrophic scarring in the rabbit ear model
Abstract
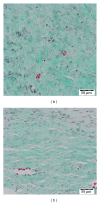
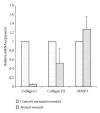
nAG (newt-Anterrior Gradient) protein is the key mediator of regrowth of amputated limbs in salamanders. In a previous work in our lab, a new nAG gene (suitable for humans) was designed and cloned. The cloned vector was transfected into primary human fibroblasts. The expression of nAG in human primary fibroblasts was found to suppress collagen expression. The current study shows that local injection of recombinant nAG reduces scar hypertrophy in the rabbit ear model. This is associated with lower scar elevation index (SEI), lower levels of collagen I & III, higher levels of MMP1, and a higher degree of scar maturation in experimental wounds compared to controls.
Figures

References
-
- Bock O, Schmid-Ott G, Malewski P, Mrowietz U. Quality of life of patients with keloid and hypertrophic scarring. Archives of Dermatological Research. 2006;297(10):433–438. - PubMed
-
- Bloemen MCT, van der Veer WM, Ulrich MMW, van Zuijlen PPM, Niessen FB, Middelkoop E. Prevention and curative management of hypertrophic scar formation. Burns. 2009;35(4):463–475. - PubMed
-
- Nikkonen MM, Pitkanen JM, Al-Qattan MM. Problems associated with the use of silicone gel sheeting for hypertrophic scars in the hot climate of Saudi Arabia. Burns. 2001;27(5):498–501. - PubMed
-
- Ledon JA, Savas J, Franca K, Chacon A, Nouri K. Intralesional treatment for keloids and hypertrophic scars: a review. Dermatologic Surgery. 2013;39(12):1745–1757. - PubMed
-
- Rahmani-Neishaboor E, Yau FM, Jalili R, Kilani RT, Ghahary A. Improvement of hypertrophic scarring by using topical anti-fibrogenic/anti-inflammatory factors in a rabbit ear model. Wound Repair and Regeneration. 2010;18(4):401–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

