Cardiac phosphoproteomics during remote ischemic preconditioning: a role for the sarcomeric Z-disk proteins
- PMID: 24795895
- PMCID: PMC3985148
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/767812
Cardiac phosphoproteomics during remote ischemic preconditioning: a role for the sarcomeric Z-disk proteins
Abstract
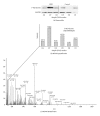
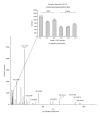
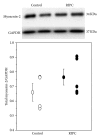
Remote ischemic preconditioning (RIPC) induced by brief ischemia/reperfusion cycles of remote organ (e.g., limb) is cardioprotective. The myocardial cellular changes during RIPC responsible for this phenomenon are not currently known. The aim of this work was to identify the activation by phosphorylation of cardiac proteins following RIPC. To achieve our aim we used isobaric tandem mass tagging (TMT) and reverse phase nanoliquid chromatography tandem spectrometry using a Linear Trap Quadropole (LTQ) Orbitrap Velos mass spectrometer. Male C57/Bl6 mice were anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of Tribromoethanol. A cuff was placed around the hind limb and inflated at 200 mmHg to prevent blood flow as confirmed by Laser Doppler Flowmetry. RIPC was induced by 4 cycles of 5 min of limb ischemia followed by 5 min of reperfusion. Hearts were extracted for phosphoproteomics. We identified approximately 30 phosphoproteins that were differentially expressed in response to RIPC protocol. The levels of several phosphoproteins in the Z-disk of the sarcomere including phospho-myozenin-2 were significantly higher than control. This study describes and validates a novel approach to monitor the changes in the cardiac phosphoproteome following the cardioprotective intervention of RIPC and prior to index ischemia. The increased level of phosphorylated sarcomeric proteins suggests they may have a role in cardiac signaling during RIPC.
Figures
References
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Remote ischaemic preconditioning: underlying mechanisms and clinical application. Cardiovascular Research. 2008;79(3):377–386. - PubMed
-
- Hoole SP, Heck PM, Sharples L, et al. Cardiac Remote Ischemic Preconditioning in Coronary Stenting (CRISP Stent) Study: a prospective, randomized control trial. Circulation. 2009;119(6):820–827. - PubMed
-
- Hoole SP, Heck PM, White PA, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning stimulus does not reduce microvascular resistance or improve myocardial blood flow in patients undergoing elective percutaneous coronary intervention. Angiology. 2009;60(4):403–411. - PubMed
-
- Botker HE, Kharbanda R, Schmidt MR, et al. Remote ischaemic conditioning before hospital admission, as a complement to angioplasty, and effect on myocardial salvage in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomised trial. The Lancet. 2010;375(9716):727–734. - PubMed
-
- Luo SJ, Zhou YJ, Shi DM, Ge HL, Wang JL, Liu RF. Remote ischemic preconditioning reduces myocardial injury in patients undergoing coronary stent implantation. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 2013;29(9):1084–1089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

