Effects of subchronic exposure to N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide on selected biomarkers in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.)
- PMID: 24795897
- PMCID: PMC3985181
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/828515
Effects of subchronic exposure to N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide on selected biomarkers in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.)
Abstract
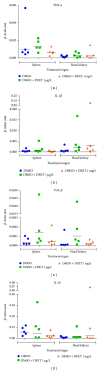
DEET (N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide) is the most common active ingredient in the insect repellents commonly detected in European groundwater. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of subchronic DEET exposure on biochemical and haematological parameters, antioxidant enzymes, including catalase, glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione S-transferase, and the amount of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Two specific proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine genes were selected to assess an immunological status of the fish. Fish were exposed for 28 days to three concentrations of DEET (1.0 µg/L, 0.1 mg/L, and 1.0 mg/L) where 1 µg/L is corresponding to the concentration found in the environment. DEET had a significant (P < 0.05) effect on increased RBC, decreased mean corpuscular volume (MCV), and mean corpuscular haemoglobin value (MCH) compared to control groups in the concentration of 1 mg/L. A significant decline (P < 0.05) in triacylglycerols (TAG) in plasma was found in the concentration of 1 mg/L compared to the control groups. The parameters of oxidative stress in tissues of common carp were weekly affected and immunological parameters were not affected.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of Click 500 SC (terbuthylazine) on common carp Cyprinus carpio under (sub)chronic conditions.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2011;32 Suppl 1:15-24. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2011. PMID: 22167222
-
The effect of the fluoroquinolone norfloxacin on somatic indices and oxidative stress parameters in early stages of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.).Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015;36 Suppl 1:79-87. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26757128
-
Effect of chronic exposure to simazine on oxidative stress and antioxidant response in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.).Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;33(2):334-43. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2011.12.019. Epub 2011 Dec 26. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22301164
-
Chlorpyrifos-induced changes in oxidant/antioxidant status and haematological parameters of Cyprinus carpio carpio: ameliorative effect of lycopene.Chemosphere. 2013 Feb;90(7):2059-64. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.12.006. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Chemosphere. 2013. PMID: 23312461 Review.
-
Assessment of the environmental fate and ecotoxicity of N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET).Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2012 Jan;8(1):120-34. doi: 10.1002/ieam.1246. Integr Environ Assess Manag. 2012. PMID: 22006575 Review.
Cited by
-
Safety Evaluation of Various Vector Repellents in Combination with Deltamethrin in Wistar Rats.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2018 Jan-Mar;10(1):21-28. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_219_17. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2018. PMID: 29657504 Free PMC article.
-
The applicability of oxidative stress biomarkers in assessing chromium induced toxicity in the fish Labeo rohita.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:782493. doi: 10.1155/2014/782493. Epub 2014 Sep 14. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 25302308 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Investigations of the Temporal Effects of Exposure to Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products and Their Mixture in the Eastern Oyster (Crassostrea virginica).Environ Toxicol Chem. 2020 Feb;39(2):419-436. doi: 10.1002/etc.4627. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31661721 Free PMC article.
-
Repellent Screening of Selected Plant Essential Oils Against Dengue Fever Mosquitoes Using Behavior Bioassays.Neotrop Entomol. 2023 Jun;52(3):521-529. doi: 10.1007/s13744-023-01039-z. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Neotrop Entomol. 2023. PMID: 36928838 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the histologic appearance of normal gill tissue using special staining techniques.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2018 Sep;30(5):688-698. doi: 10.1177/1040638718791819. Epub 2018 Jul 20. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2018. PMID: 30029586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robbins PJ, Cherniack MG. Review of the biodistribution and toxicity of the insect repellent N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health. 1986;18(4):503–525. - PubMed
-
- McConnell R, Fidler AT, Chrislip D. 83-085. Washington, DC, USA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, NIOSH; 1986. Health Hazard Evaluation Determination.
-
- Fradin MS, Day JF. Comparative efficacy of insect repellents against mosquito bites. New England Journal of Medicine. 2002;347(1):13–18. - PubMed
-
- Osimitz TG, Murphy JV, Fell LA, Page B. Adverse events associated with the use of insect repellents containing N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology. 2010;56(1):93–99. - PubMed
-
- Costanzo SD, Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Kolpin DW, Sandstrom MW. Is there a risk associated with the insect repellent DEET (N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide) commonly found in aquatic environments? Science of the Total Environment. 2007;384(1–3):214–220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials