One-stage hip reconstruction in children with cerebral palsy: long-term results at skeletal maturity
- PMID: 24796563
- PMCID: PMC4142890
- DOI: 10.1007/s11832-014-0589-9
One-stage hip reconstruction in children with cerebral palsy: long-term results at skeletal maturity
Abstract
Purpose: Hip subluxation is common in children with cerebral palsy (CP). Surgery is indicated in case of pain or progressive increase of Reimers index on radiographs. Peri-iliac osteotomy combined with femoral osteotomy is one of the numerous operative techniques available, but results at skeletal maturity remain unclear. The purpose of this radiological study was to report the long-term results of this procedure.
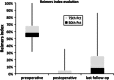
Materials and methods: Twenty hips in 20 children were retrospectively evaluated at skeletal maturity. Mean age at surgery was 8.1 years and follow-up averaged 9.1 years. All patients underwent Dega acetabuloplasty, soft-tissue release and femoral-shortening varus derotation osteotomy without open reduction. Reimers index, acetabular angle (AA) and neck-shaft angle (NSA) were compared on preoperative, postoperative and latest follow-up radiographs.
Results: Dega osteotomy significantly improved the AA and the correction remained stable at maturity. The NSA significantly decreased postoperatively (153°-115°), but recurrence of the valgus deformity (130°) of the proximal femur was observed at maturity. Consequently, Reimers index followed the same evolution. No case of osteonecrosis was reported but one hip dislocated and one subluxated during follow-up.
Conclusion: Progressive recurrence of the valgus deformity of the proximal femur, attributable to adductors spasticity and gluteus medius weakness, led to a significant increase in the Reimers index. However, hip coverage remained >70 % at maturity in 90 % of the hips. This one-stage procedure without hip dislocation efficaciously corrected acetabulum dysplasia and successfully treated neurological hips in CP patients.
Level of evidence iv: retrospective study.
Figures




References
-
- Noonan KJ, Walker TL, Kayes KJ, et al. Varus derotation osteotomy for the treatment of hip subluxation and dislocation in cerebral palsy: statistical analysis in 73 hips. J Pediatr Orthop Part B. 2001;10(4):279–286. - PubMed
-
- Mubarak SJ, Valencia FG, Wenger DR. One-stage correction of the spastic dislocated hip. Use of pericapsular acetabuloplasty to improve coverage. J Bone Jt Surg. 1992;74(9):1347–1357. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

