HIF-1α/COX-2 expression and mouse brain capillary remodeling during prolonged moderate hypoxia and subsequent re-oxygenation
- PMID: 24796880
- PMCID: PMC4066660
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.04.035
HIF-1α/COX-2 expression and mouse brain capillary remodeling during prolonged moderate hypoxia and subsequent re-oxygenation
Abstract
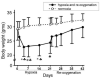
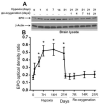
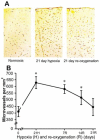
Dynamic microvascular remodeling maintains an optimal continuous supply of oxygen and nutrients to the brain to account for prolonged environmental variations. The objective of this study was to determine the relative time course of capillary regression during re-oxygenation after exposure to prolonged moderate hypoxia and expression of the primary signaling factors involved in the process. Four-month old male C57BL/6 mice were housed and maintained in a hypobaric chamber at 290 Torr (0.4 atm) for 21 days and allowed to recover at normoxia (room air) for up to 21 days. The mice were either decapitated or perfused in-situ and brain samples collected were either homogenized for Western blot analysis or fixed and embedded in paraffin for immunohistochemistry. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and erythropoietin (EPO) expression were increased during hypoxic exposure and diminished during subsequent re-oxygenation. However, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) were both elevated during hypoxia as well as subsequent re-oxygenation. Significantly increased capillary density at the end of the 3rd week of hypoxia regressed back toward normoxic baseline as the duration of re-oxygenation continued. In conclusion, elevated COX-2 and Ang-2 expression during hypoxia where angiogenesis occurs and re-oxygenation, when micro-vessels regress, identifies these proteins as vascular remodeling molecules crucial for angioplasticity.
Keywords: Ang-2; Brain capillary remodeling; EPO; VEGF.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
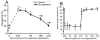


Similar articles
-
Increased HIF-1α and HIF-2α accumulation, but decreased microvascular density, in chronic hyperoxia and hypercapnia in the mouse cerebral cortex.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;789:29-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7411-1_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23852473
-
Decreased VEGF expression and microvascular density, but increased HIF-1 and 2α accumulation and EPO expression in chronic moderate hyperoxia in the mouse brain.Brain Res. 2012 Aug 30;1471:46-55. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.06.055. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22820296 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences in hypoxic acclimatization in cyclooxygenase-2-deficient mice.Physiol Rep. 2017 Feb;5(4):e13148. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13148. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28242826 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis is delayed in aging mouse brain.Brain Res. 2011 May 10;1389:50-60. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.016. Epub 2011 Mar 12. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21402058 Free PMC article.
-
Erythropoietin and the hypoxic brain.J Exp Biol. 2004 Aug;207(Pt 18):3233-42. doi: 10.1242/jeb.01049. J Exp Biol. 2004. PMID: 15299044 Review.
Cited by
-
Physiological and Pathological Remodeling of Cerebral Microvessels.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 21;23(20):12683. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012683. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manipulation of iron status on cerebral blood flow at high altitude in lowlanders and adapted highlanders.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023 Jul;43(7):1166-1179. doi: 10.1177/0271678X231152734. Epub 2023 Mar 8. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2023. PMID: 36883428 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase inhibition attenuates brain angiogenesis and independently decreases mouse survival under hypoxia.J Neurochem. 2021 Jul;158(2):246-261. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15291. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33389746 Free PMC article.
-
The evidence for the physiological effects of lactate on the cerebral microcirculation: a systematic review.J Neurochem. 2019 Mar;148(6):712-730. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14633. Epub 2019 Jan 24. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 30472728 Free PMC article.
-
Brain adaptation to hypoxia and hyperoxia in mice.Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.10.018. Epub 2016 Nov 4. Redox Biol. 2017. PMID: 27835780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

