Glutaminase 2 negatively regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling and shows tumor suppression activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 24797434
- PMCID: PMC4058033
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.1862
Glutaminase 2 negatively regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling and shows tumor suppression activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
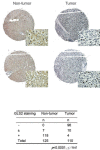
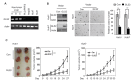
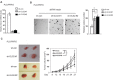
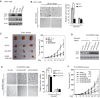
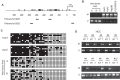
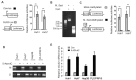
The tumor suppressor p53 and its signaling pathway play a critical role in tumor prevention. As a direct p53 target gene, the role of glutaminase 2 (GLS2) in tumorigenesis is unclear. In this study, we found that GLS2 expression is significantly decreased in majority of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Restoration of GLS2 expression in HCC cells inhibits the anchorage-independent growth of cells and reduces the growth of HCC xenograft tumors. Interestingly, we found that GLS2 negatively regulates the PI3K/AKT signaling, which is frequently activated in HCC. Blocking the PI3K/AKT signaling in HCC cells largely abolishes the inhibitory effect of GLS2 on the anchorage-independent cell growth and xenograft tumor growth. The GLS2 promoter is hypermethylated in majority of HCC samples. CpG methylation of GLS2 promoter inhibits GLS2 transcription, whereas reducing the methylation of GLS2 promoter induces GLS2 expression. Taken together, our results demonstrate that GLS2 plays an important role in tumor suppression in HCC, and the negative regulation of PI3K/AKT signaling contributes greatly to this function of GLS2. Furthermore, hypermethylation of GLS2 promoter is an important mechanism contributing to the decreased GLS2 expression in HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Levine AJ, Hu W, Feng Z. The P53 pathway: what questions remain to be explored? Cell Death Differ. 2006;13(6):1027–1036. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Prives C. Blinded by the Light: The Growing Complexity of p53. Cell. 2009;137(3):413–431. - PubMed
-
- Greenblatt MS, Bennett WP, Hollstein M, Harris CC. Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 1994;54(18):4855–4878. - PubMed
-
- Staib F, Hussain SP, Hofseth LJ, Wang XW, Harris CC. TP53 and liver carcinogenesis. Hum Mutat. 2003;21(3):201–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

