Apamin does not inhibit human cardiac Na+ current, L-type Ca2+ current or other major K+ currents
- PMID: 24798465
- PMCID: PMC4010514
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096691
Apamin does not inhibit human cardiac Na+ current, L-type Ca2+ current or other major K+ currents
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e104445.
Abstract
Background: Apamin is commonly used as a small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (SK) current inhibitor. However, the specificity of apamin in cardiac tissues remains unclear.
Objective: To test the hypothesis that apamin does not inhibit any major cardiac ion currents.
Methods: We studied human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells that expressed human voltage-gated Na+, K+ and Ca2+ currents and isolated rabbit ventricular myocytes. Whole-cell patch clamp techniques were used to determine ionic current densities before and after apamin administration.
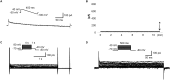
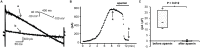
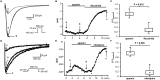
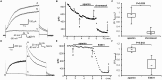
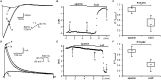
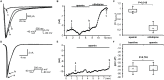
Results: Ca2+ currents (CACNA1c+CACNB2b) were not affected by apamin (500 nM) (data are presented as median [25th percentile;75th percentile] (from -16 [-20;-10] to -17 [-19;-13] pA/pF, P = NS), but were reduced by nifedipine to -1.6 [-3.2;-1.3] pA/pF (p = 0.008). Na+ currents (SCN5A) were not affected by apamin (from -261 [-282;-145] to -268 [-379;-132] pA/pF, P = NS), but were reduced by flecainide to -57 [-70;-47] pA/pF (p = 0.018). None of the major K+ currents (IKs, IKr, IK1 and Ito) were inhibited by 500 nM of apamin (KCNQ1+KCNE1, from 28 [20]; [37] to 23 [18]; [32] pA/pF; KCNH2+KCNE2, from 28 [24]; [30] to 27 [24]; [29] pA/pF; KCNJ2, from -46 [-48;-40] to -46 [-51;-35] pA/pF; KCND3, from 608 [505;748] to 606 [454;684]). Apamin did not inhibit the INa or ICaL in isolated rabbit ventricular myocytes (INa, from -67 [-75;-59] to -68 [-71;-59] pA/pF; ICaL, from -16 [-17;-14] to -14 [-15;-13] pA/pF, P = NS for both).
Conclusions: Apamin does not inhibit human cardiac Na+ currents, L-type Ca2+ currents or other major K+ currents. These findings indicate that apamin is a specific SK current inhibitor in hearts as well as in other organs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kohler M, Hirschberg B, Bond CT, Kinzie JM, Marrion NV, et al. (1996) Small-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channels from mammalian brain. Science 273: 1709–1714. - PubMed
-
- Castle NA, Haylett DG, Jenkinson DH (1989) Toxins in the characterization of potassium channels. Trends Neurosci 12: 59–65. - PubMed
-
- Ishii TM, Maylie J, Adelman JP (1997) Determinants of apamin and d-tubocurarine block in SK potassium channels. J Biol Chem 272: 23195–23200. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Tuteja D, Zhang Z, Xu D, Zhang Y, et al. (2003) Molecular identification and functional roles of a Ca2+-activated K+ channel in human and mouse hearts. J Biol Chem 278: 49085–49094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

