Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Pioglitazone on Lipid Metabolism in Obese Diabetic KKAy Mice
- PMID: 24799887
- PMCID: PMC3988943
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/538183
Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Pioglitazone on Lipid Metabolism in Obese Diabetic KKAy Mice
Abstract
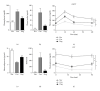
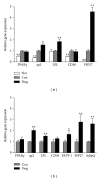
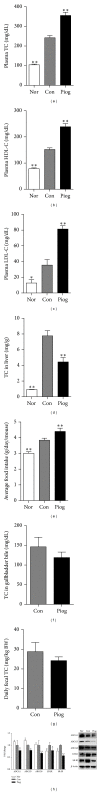
This study aimed to analyze the effects and potential mechanisms of pioglitazone on triglyceride and cholesterol metabolism in obese diabetic KKAy mice. Pioglitazone was orally administered to KKAy mice over 30 days. Compared to C57BL/6J mice, KKAy mice developed obvious insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, and hyperlipidemia. Pioglitazone treatment resulted in deteriorated microvesicular steatosis and elevated hepatic triglyceride levels, though plasma triglyceride and free fatty acid levels were reduced by the treatment, compared to nontreated KKAy mice. Plasma alanine aminotransferase activities were also significantly increased. Additionally, pioglitazone increased plasma concentrations of total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol but decreased hepatic cholesterol. Gene expression profiling revealed that pioglitazone stimulated hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma hyperactivity, and induced the upregulation of adipocyte-specific and lipogenesis-related genes but downregulated of genes involved in triglyceride lipolysis and fatty acid β -oxidation. Pioglitazone also regulated the genes expression of hepatic cholesterol uptake and excretion, such as low density lipoprotein receptor (LDL-R) and scavenger receptor type-BI (SR-BI). These results suggested that pioglitazone could induce excessive hepatic triglyceride accumulation, thus aggravating liver steatosis and lesions in KKAy mice. Furthermore, pioglitazone may suppress the clearance of serum cholesterol from the liver predominantly through inhibition of LDL-R and SR-BI expression, thus increasing the plasma cholesterol.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mixture of five herbal extracts ameliorates pioglitazone-induced aggravation of hepatic steatosis via activating the adiponectin receptor 2/AMP-activated protein kinase signal pathway in diabetic KKAy mice.J Tradit Chin Med. 2017 Oct;37(5):588-598. J Tradit Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 32188218
-
Intraperitoneal administration attenuates thiazolidinedione-induced hepatic steatosis in KKAy mice with increased hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ mRNA expression.Obes Res Clin Pract. 2012 Jul-Sep;6(3):e175-262. doi: 10.1016/j.orcp.2011.10.004. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2012. PMID: 24331528
-
Diabetic KKAy mice exhibit increased hepatic PPARgamma1 gene expression and develop hepatic steatosis upon chronic treatment with antidiabetic thiazolidinediones.J Hepatol. 2001 Jul;35(1):17-23. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(01)00066-6. J Hepatol. 2001. PMID: 11495036
-
[Insulin resistance-reducing effect of a new thiazolidinedione derivative, pioglitazone].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001 May;117(5):335-42. doi: 10.1254/fpj.117.335. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11411343 Review. Japanese.
-
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Dyslipidemia.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018 Sep 1;25(9):771-782. doi: 10.5551/jat.RV17023. Epub 2018 Jul 12. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018. PMID: 29998913 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of a ready-to-eat cereal formula powder on glucose metabolism, inflammation, and gut microbiota in diabetic db/db mice.Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Jun 29;8(8):4523-4533. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1761. eCollection 2020 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32884732 Free PMC article.
-
Diphenyl Diselenide Alleviates Tert-Butyl Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Rat Glomerular Mesangial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 23;23(19):11215. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911215. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232514 Free PMC article.
-
Xenobiotic-Induced Aggravation of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1062. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031062. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35162986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rosiglitazone Requires Hepatocyte PPARγ Expression to Promote Steatosis in Male Mice With Diet-Induced Obesity.Endocrinology. 2021 Nov 1;162(11):bqab175. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqab175. Endocrinology. 2021. PMID: 34417811 Free PMC article.
-
Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia Predicts Development of Insulin Resistance Glucose Intolerance and Type 2 Diabetes.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 25;11(1):e0145730. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145730. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26808523 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chitturi S, Abeygunasekera S, Farrell GC, et al. NASH and insulin resistance: insulin hypersecretion and specific association with the insulin resistance syndrome. Hepatology. 2002;35(2):373–379. - PubMed
-
- Smith BW, Adams LA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus: pathogenesis and treatment. Nature Reviews Endocrinology. 2011;7(8):456–465. - PubMed
-
- Tailleux A, Wouters K, Staels B. Roles of PPARs in NAFLD: potential therapeutic targets. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2012;1821(5):809–818. - PubMed
-
- Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;355(22):2297–2307. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

