Gross and Morphometric Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System of Bats (Eidolon helvum)
- PMID: 24800105
- PMCID: PMC3988946
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/358158
Gross and Morphometric Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System of Bats (Eidolon helvum)
Abstract
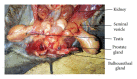
The present study aimed at examining the gross and morphometry of the reproductive tract of the male bats (Eidolon helvum). Thirty male bats (adults n = 17 and juveniles n = 13) were captured using net, weighed, aged using relative ossification of the wing bone, and dissected for gross examination. Morphologically, the mean body weight and forearm length in both adults and juveniles were 235.31 ± 6.30 g, 12.14 ± 0.19 cm and 69.54 ± 7.68 g, 7.77 ± 0.29 cm, respectively. The testicles were completely descended in adults with the penis projected cranially. The epididymides were found at the median border of the testis and continues as vas deferens. No significant differences (P > 0.05) were observed between right and left testicular weights in both adults and juveniles and also in lengths of different parts of the reproductive segments in both age groups assessed, respectively. This work has documented the gross anatomy of the male reproductive tract in bats. Ultrastructure and histochemistry are recommended for further insight into the reproductive biology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Haematological Studies and Micronucleus Assay of Straw-Coloured Fruit Bats (Eidolon helvum).Niger J Physiol Sci. 2020 Dec 31;35(2):181-186. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2020. PMID: 34009208
-
Gross Morphometric Studies on the Tongue, Buccal Cavity and Hard Palate of the Fruit Bat (Eidolon helvum).Anat Histol Embryol. 2015 Aug;44(4):283-7. doi: 10.1111/ahe.12138. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Anat Histol Embryol. 2015. PMID: 25115593
-
NTP technical report on the toxicity studies of Dibutyl Phthalate (CAS No. 84-74-2) Administered in Feed to F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice.Toxic Rep Ser. 1995 Apr;30:1-G5. Toxic Rep Ser. 1995. PMID: 12209194
-
Aspects of the Macroscopic Testicular and Epididymal Morphology in the Greater Rhea, Rhea Americana (Linneaus - 1758) Birds.Anat Histol Embryol. 2015 Aug;44(4):255-61. doi: 10.1111/ahe.12133. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Anat Histol Embryol. 2015. PMID: 25091030
-
Lagos Bat Virus Infection Dynamics in Free-Ranging Straw-Colored Fruit Bats (Eidolon helvum).Trop Med Infect Dis. 2017 Jul 8;2(3):25. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed2030025. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 30270883 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Morphological and Histological Variations of the Reproductive Organs During the Annual Cycle in a Neotropical Bat: Peters' Ghost-Faced Bat Mormoops megalophylla (Chiroptera: Mormoopidae).J Morphol. 2025 Jul;286(7):e70066. doi: 10.1002/jmor.70066. J Morphol. 2025. PMID: 40665677 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructure of the secretory epithelial cells of the Cowper's gland in the Indian fruit bat, Rousettus leschenaulti (Desmarest) during the reproductive cycle.J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2016 Jul-Sep;4(3):156-161. doi: 10.1016/j.jmau.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Microsc Ultrastruct. 2016. PMID: 30023222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Riede K. Final Report of R and D Projekt. 808 05 081. Federal Agency of Nature Conservation; 2004. Global register of migratory species: from global region.
-
- Bat Conservation International. Bat facts and Amazing Trivia. Beaufortia. 1997;40:111–177.
-
- Barclay RMR, Harder LD. Life histories of bats: life in the slow lane. In: Kunz TH, Fenton MB, editors. Bat Ecology University of Chicago Press. Chicago, Ill, USA: 2003. pp. 209–253.
-
- Mickleburgh SP, Hutson AM, Racey PA. Old World Fruit Bats: An Action plan for Their Conservation. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN; 1992.
-
- Tilmann C, Capel B. Mesonephric cell migration induces testis cord formation and Sertoli cell differentiation in the mammalian gonad. Development. 1999;126(13):2883–2890. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

