Reduced gamma oscillations in a mouse model of intellectual disability: a role for impaired repetitive neurotransmission?
- PMID: 24800744
- PMCID: PMC4011727
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095871
Reduced gamma oscillations in a mouse model of intellectual disability: a role for impaired repetitive neurotransmission?
Abstract
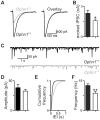
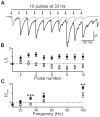
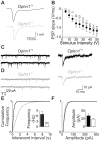
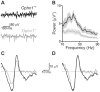
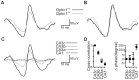
Intellectual disability affects 2-3% of the population; mutations of the X-chromosome are a major cause of moderate to severe cases. The link between the molecular consequences of the mutation and impaired cognitive function remains unclear. Loss of function mutations of oligophrenin-1 (OPHN1) disrupt Rho-GTPase signalling. Here we demonstrate abnormal neurotransmission at CA3 synapses in hippocampal slices from Ophn1-/y mice, resulting from a substantial decrease in the readily releasable pool of vesicles. As a result, synaptic transmission fails at high frequencies required for oscillations associated with cognitive functions. Both spontaneous and KA-induced gamma oscillations were reduced in Ophn1-/y hippocampal slices. Spontaneous oscillations were rapidly rescued by inhibition of the downstream signalling pathway of oligophrenin-1. These findings suggest that the intellectual disability due to mutations of oligophrenin-1 results from a synaptopathy and consequent network malfunction, providing a plausible mechanism for the learning disabilities. Furthermore, they raise the prospect of drug treatments for affected individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Chelly J, Khelfaoui M, Francis F, Cherif B, Bienvenu T (2006) Genetics and pathophysiology of mental retardation. Eur J HumGenet 14: 701–713. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi V, Farisello P, Baldelli P, Meskenaite V, Milanese M, et al. (2009) Cognitive impairment in Gdi1 deficient mice is associated with altered synaptic vesicle pools and short-term synaptic plasticity, and can be corrected by appropriate learning training. Human Molecular Genetics 18: 105–117. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Herrmann CS, Munk MH, Engel AK (2004) Cognitive functions of gamma-band activity: memory match and utilization. Trends Cogn Sci 8: 347–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

