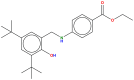
Gastroprotective activity of ethyl-4-[(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzylidene) amino]benzoate against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal ulcer in rats
- PMID: 24800807
- PMCID: PMC4011731
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095908
Gastroprotective activity of ethyl-4-[(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzylidene) amino]benzoate against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal ulcer in rats
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Gastroprotective Activity of Ethyl-4-[(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzylidene) Amino]benzoate against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Ulcer in Rats.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 10;18(11):e0294007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294007. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37948322 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The study was carried out to determine the cytotoxic, antioxidant and gastro-protective effect of ethyl-4-[(3,5-di-tert-butyl-2-hydroxybenzylid ene)amino] benzoate (ETHAB) in rats.
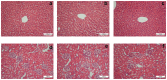
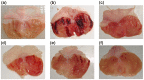
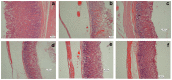
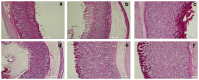
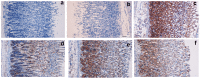
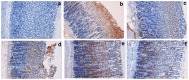
Methodology/principal findings: The cytotoxic effect of ETHAB was assessed using a MTT cleavage assay on a WRL68 cell line, while its antioxidant activity was evaluated in vitro. In the anti-ulcer study, rats were divided into six groups. Group 1 and group 2 received 10% Tween 20 (vehicle). Group 3 received 20 mg/kg Omeprazole. Groups 4, 5 and 6 received ETHAB at doses of 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg, respectively. After an hour, group 1 received the vehicle. Groups 2-6 received absolute ethanol to induce gastric mucosal lesions. In the WRL68 cell line, an IC50 of more than 100 µg/mL was observed. ETHAB results showed antioxidant activity in the DPPH, FRAP, nitric oxide and metal chelating assays. There was no acute toxicity even at the highest dosage (1000 mg/kg). Microscopy showed that rats pretreated with ETHAB revealed protection of gastric mucosa as ascertained by significant increases in superoxide dismutase (SOD), pH level, mucus secretion, reduced gastric lesions, malondialdehyde (MDA) level and remarkable flattened gastric mucosa. Histologically, pretreatment with ETHAB resulted in comparatively better gastric protection, due to reduction of submucosal edema with leucocyte infiltration. PAS staining showed increased intensity in uptake of Alcian blue. In terms of immunohistochemistry, ETHAB showed down-expression of Bax proteins and over-expression of Hsp70 proteins.
Conclusion/significance: The gastroprotective effect of ETHAB may be attributed to antioxidant activity, increased gastric wall mucus, pH level of gastric contents, SOD activity, decrease in MDA level, ulcer area, flattening of gastric mucosa, reduction of edema and leucocyte infiltration of the submucosal layer, increased PAS staining, up-regulation of Hsp70 protein and suppressed expression of Bax.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
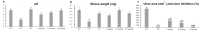
References
-
- Thalamuthu S, Annaraj B, Neelakantan MA (2014) A systematic investigation on biological activities of a novel double zwitterionic Schiff base Cu(II) complex. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 118: 120–129. - PubMed
-
- Raweh S, Bayach I, Taha M, Baharudin MS, Di Meo F, et al. (2013) Antioxidant properties of phenolic Schiff bases: structure–activity relationship and mechanism of action. Journal of Computer-aided Molecular Design 27: 951–964. - PubMed
-
- El-Nawawy MA, Farag RS, Sbbah IA, Abu-Yamin A-AM (2011) Spectroscopic studies, crystal structure and biological activity of {ethyl 4-(2-hydroxy-benzylideneamino) benzoate} schiff base and its copper complex. New York Science Journal 4: 78–82.
-
- Ganguly A, Chakraborty P, Banerjee K, Choudhuri SK (2014) The role of a Schiff base scaffold, N-(2-hydroxy acetophenone) glycinate-in overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 51: 96–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

