Entrainment to periodic initiation and transition rates in a computational model for gene translation
- PMID: 24800863
- PMCID: PMC4011696
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096039
Entrainment to periodic initiation and transition rates in a computational model for gene translation
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e101909
Abstract
Periodic oscillations play an important role in many biomedical systems. Proper functioning of biological systems that respond to periodic signals requires the ability to synchronize with the periodic excitation. For example, the sleep/wake cycle is a manifestation of an internal timing system that synchronizes to the solar day. In the terminology of systems theory, the biological system must entrain or phase-lock to the periodic excitation. Entrainment is also important in synthetic biology. For example, connecting several artificial biological systems that entrain to a common clock may lead to a well-functioning modular system. The cell-cycle is a periodic program that regulates DNA synthesis and cell division. Recent biological studies suggest that cell-cycle related genes entrain to this periodic program at the gene translation level, leading to periodically-varying protein levels of these genes. The ribosome flow model (RFM) is a deterministic model obtained via a mean-field approximation of a stochastic model from statistical physics that has been used to model numerous processes including ribosome flow along the mRNA. Here we analyze the RFM under the assumption that the initiation and/or transition rates vary periodically with a common period T. We show that the ribosome distribution profile in the RFM entrains to this periodic excitation. In particular, the protein synthesis pattern converges to a unique periodic solution with period T. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first proof of entrainment in a mathematical model for translation that encapsulates aspects such as initiation and termination rates, ribosomal movement and interactions, and non-homogeneous elongation speeds along the mRNA. Our results support the conjecture that periodic oscillations in tRNA levels and other factors related to the translation process can induce periodic oscillations in protein levels, and may suggest a new approach for re-engineering genetic systems to obtain a desired, periodic, protein synthesis rate.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
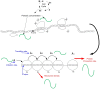
 -periodic, for example, due to signals related to the cell-cycle. Lower part: in the RFM, this is modeled by
-periodic, for example, due to signals related to the cell-cycle. Lower part: in the RFM, this is modeled by  -periodic rates
-periodic rates  and
and  yielding the PRFM. Our main result shows that consequently the translation rate and ribosomal densities (the
yielding the PRFM. Our main result shows that consequently the translation rate and ribosomal densities (the  s) converge to a unique
s) converge to a unique  -periodic solution.
-periodic solution.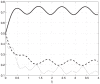
 .
.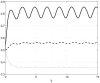
 , while the transition rates are constant and relatively small. All state-variable converge to a periodic signal with period
, while the transition rates are constant and relatively small. All state-variable converge to a periodic signal with period  , but the amplitude of the oscillations is considerably attenuated as it passes through the mRNA chain.
, but the amplitude of the oscillations is considerably attenuated as it passes through the mRNA chain.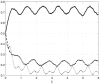
 , but with added random noise. It may be seen that each state-variable converges to a periodic signal with period
, but with added random noise. It may be seen that each state-variable converges to a periodic signal with period  , but with added noise.
, but with added noise.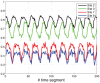
Similar articles
-
Ribosome flow model with extended objects.J R Soc Interface. 2017 Oct;14(135):20170128. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2017.0128. J R Soc Interface. 2017. PMID: 29021157 Free PMC article.
-
On the gain of entrainment in the n-dimensional ribosome flow model.J R Soc Interface. 2023 Feb;20(199):20220763. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0763. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J R Soc Interface. 2023. PMID: 36751928 Free PMC article.
-
Maximizing protein translation rate in the non-homogeneous ribosome flow model: a convex optimization approach.J R Soc Interface. 2014 Nov 6;11(100):20140713. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0713. J R Soc Interface. 2014. PMID: 25232050 Free PMC article.
-
Entrainment of the human circadian system by light.J Biol Rhythms. 2005 Aug;20(4):326-38. doi: 10.1177/0748730405277983. J Biol Rhythms. 2005. PMID: 16077152 Review.
-
Controlling translation elongation efficiency: tRNA regulation of ribosome flux on the mRNA.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Feb;42(1):160-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20130132. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 24450645 Review.
Cited by
-
Translation in the cell under fierce competition for shared resources: a mathematical model.J R Soc Interface. 2022 Dec;19(197):20220535. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0535. Epub 2022 Dec 21. J R Soc Interface. 2022. PMID: 36541059 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome flow model with extended objects.J R Soc Interface. 2017 Oct;14(135):20170128. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2017.0128. J R Soc Interface. 2017. PMID: 29021157 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive biophysical modeling and understanding of the dynamics of mRNA translation and its evolution.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Nov 2;44(19):9031-9049. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw764. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27591251 Free PMC article.
-
Networks of ribosome flow models for modeling and analyzing intracellular traffic.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 8;9(1):1703. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37864-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30737417 Free PMC article.
-
Controllability Analysis and Control Synthesis for the Ribosome Flow Model.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2018 Jul-Aug;15(4):1351-1364. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2707420. Epub 2017 May 23. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 28541906 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

