Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of O-2-modified indenoisoquinolines as dual topoisomerase I-tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I inhibitors
- PMID: 24800942
- PMCID: PMC4033654
- DOI: 10.1021/jm500294a
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of O-2-modified indenoisoquinolines as dual topoisomerase I-tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I inhibitors
Abstract
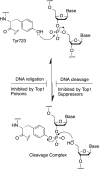
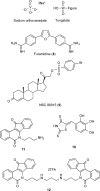
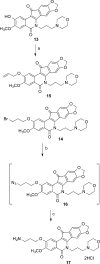
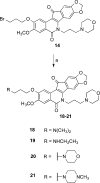
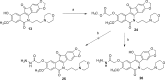
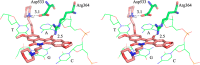
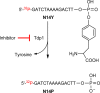
Tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (TDP1) repairs stalled topoisomerase I (Top1)-DNA covalent complexes and has been proposed to be a promising and attractive target for cancer treatment. Inhibitors of TDP1 could conceivably act synergistically with Top1 inhibitors and thereby potentiate the effects of Top1 poisons. This study describes the successful design and synthesis of 2-position-modified indenoisoquinolines as dual Top1-TDP1 inhibitors using a structure-based drug design approach. Enzyme inhibition studies indicate that indenoisoquinolines modified at the 2-position with three-carbon side chains ending with amino substituents show both promising Top1 and TDP1 inhibitory activity. Molecular modeling of selected target compounds bound to Top1 and TDP1 was used to rationalize the enzyme inhibition results and structure-activity relationship analysis.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of indenoisoquinolines that inhibit both tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (Tdp1) and topoisomerase I (Top1).J Med Chem. 2013 Jan 10;56(1):182-200. doi: 10.1021/jm3014458. Epub 2012 Dec 21. J Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23259865 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of nitrated 7-, 8-, 9-, and 10-hydroxyindenoisoquinolines as potential dual topoisomerase I (Top1)-tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (TDP1) inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2015 Apr 9;58(7):3188-208. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00136. Epub 2015 Mar 26. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25811317 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of the first dual tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase I (Tdp1)-topoisomerase I (Top1) inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2012 May 10;55(9):4457-78. doi: 10.1021/jm300335n. Epub 2012 Apr 26. J Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22536944 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 (Tdp1) inhibitors.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011 Sep;21(9):1285-92. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2011.604314. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2011. PMID: 21843105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual DNA topoisomerase 1 and tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 1 inhibition for improved anticancer activity.Med Res Rev. 2019 Jul;39(4):1427-1441. doi: 10.1002/med.21587. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Med Res Rev. 2019. PMID: 31004352 Review.
Cited by
-
New Deoxycholic Acid Derived Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 1 Inhibitors Also Inhibit Tyrosyl-DNA Phosphodiesterase 2.Molecules. 2021 Dec 23;27(1):72. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010072. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011303 Free PMC article.
-
Indenopyrans - synthesis and photoluminescence properties.Beilstein J Org Chem. 2016 Apr 27;12:825-34. doi: 10.3762/bjoc.12.81. eCollection 2016. Beilstein J Org Chem. 2016. PMID: 27340473 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of new fluorinated and chlorinated indenoisoquinoline topoisomerase I poisons.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Apr 1;24(7):1469-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.02.015. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26906474 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual-Sensor-Based Screening System for In Vitro Selection of TDP1 Inhibitors.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Jul 15;21(14):4832. doi: 10.3390/s21144832. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34300575 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Pterostilbene, a Natural Derivative of Resveratrol, in the Treatment of Colorectal Cancer through Top1/Tdp1-Mediated DNA Repair Pathway.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 9;13(16):4002. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164002. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439157 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I Inhibitors: Camptothecins and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 789–802. - PubMed
-
- Champoux J. J. DNA Topoisomerases: Structure, Function, and Mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 369–413. - PubMed
-
- Stewart L.; Redinbo M. R.; Qiu X.; Hol W. G. J.; Champoux J. J. A Model for the Mechanism of Human Topoisomerase I. Science 1998, 279, 1534–1541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials

