Acupuncture for epilepsy
- PMID: 24801225
- PMCID: PMC10105317
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005062.pub4
Acupuncture for epilepsy
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture is increasingly used in people with epilepsy. It remains unclear whether existing evidence is rigorous enough to support its use. This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in 2008.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture in people with epilepsy.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Epilepsy Group Specialised Register (June 2013) and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) in The Cochrane Library (2013, Issue 5), MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL, AMED and other databases (from inception to June 2013). We reviewed reference lists from relevant trials. We did not impose any language restrictions.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing acupuncture with placebo or sham treatment, antiepileptic drugs or no treatment; or comparing acupuncture plus other treatments with the same other treatments, involving people of any age with any type of epilepsy.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by The Cochrane Collaboration.
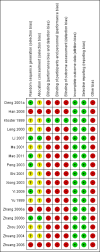
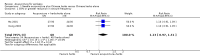
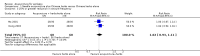
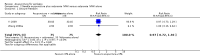
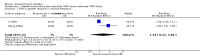
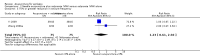
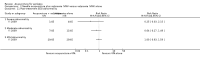
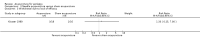
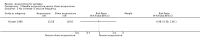
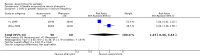
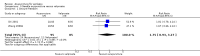
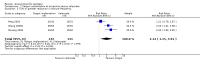
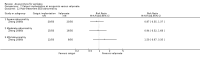
Main results: We included 17 RCTs with 1538 participants that had a wide age range and were suffering mainly from generalized epilepsy. The duration of treatment varied from 7.5 weeks to 1 year. All included trials had a high risk of bias with short follow-up. Compared with Chinese herbs, needle acupuncture plus Chinese herbs was not effective in achieving at least 50% reduction in seizure frequency (80% in control group versus 90% in intervention group, RR 1.13, 95% CI 0.97 to 1.31, 2 trials; assumed risk 500 per 1000, corresponding risk 485 to 655 per 1000). Compared with valproate, needle acupuncture plus valproate was not effective in achieving freedom from seizures (44% in control group versus 42.7% in intervention group, RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.72 to 1.30, 2 trials; assumed risk 136 per 1000, corresponding risk 97 to 177 per 1000) or at least 50% reduction in seizure frequency (69.3% in control group versus 81.3% in intervention group, RR 1.34, 95% CI 0.52 to 3.48, 2 trials; assumed risk 556 per 1000, corresponding risk 289 to 1000 per 1000) but may have achieved better quality of life (QOL) after treatment (QOLIE-31 score (higher score indicated better QOL) mean 170.22 points in the control group versus 180.32 points in the intervention group, MD 10.10 points, 95% CI 2.51 to 17.69 points, 1 trial). Compared with phenytoin, needle acupuncture was not effective in achieving at least 50% reduction in seizure frequency (70% in control group versus 94.4% in intervention group, RR 1.43, 95% CI 0.46 to 4.44, 2 trials; assumed risk 700 per 1000, corresponding risk 322 to 1000 per 1000). Compared with valproate, needle acupuncture was not effective in achieving seizure freedom (14.1% in control group versus 25.2% in intervention group, RR 1.75, 95% CI 0.93 to 3.27, 2 trials; assumed risk 136 per 1000, corresponding risk 126 to 445 per 1000) but may be effective in achieving at least 50% reduction in seizure frequency (55.3% in control group versus 73.7% in intervention group, RR 1.32, 95% CI 1.05 to 1.66, 2 trials; assumed risk 556 per 1000, corresponding risk 583 to 923 per 1000) and better QOL after treatment (QOLIE-31 score mean 172.6 points in the control group versus 184.64 points in the intervention group, MD 12.04 points, 95% CI 4.05 to 20.03 points, 1 trial). Compared with antiepileptic drugs, catgut implantation at acupoints plus antiepileptic drugs was not effective in achieving seizure freedom (13% in control group versus 19.6% in intervention group, RR 1.51, 95% CI 0.93 to 2.43, 4 trials; assumed risk 127 per 1000, corresponding risk 118 to 309 per 1000) but may be effective in achieving at least 50% reduction in seizure frequency (63.1% in control group versus 82% in intervention group, RR 1.42, 95% CI 1.07 to 1.89, 5 trials; assumed risk 444 per 1000, corresponding risk 475 to 840 per 1000) and better QOL after treatment (QOLIE-31 score (higher score indicated worse quality of life) mean 53.21 points in the control group versus 45.67 points in the intervention group, MD -7.54 points, 95% CI -14.47 to -0.61 points, 1 trial). Compared with valproate, catgut implantation may be effective in achieving seizure freedom (8% in control group versus 19.7% in intervention group, RR 2.82, 95% CI 1.61 to 4.94, 4 trials; assumed risk 82 per 1000, corresponding risk 132 to 406 per 1000) and better QOL after treatment (QOLIE-31 score (higher score indicated better quality of life) mean 172.6 points in the control group versus 191.33 points in the intervention group, MD 18.73 points, 95% CI 11.10 to 26.36 points, 1 trial) but not at least 50% reduction in seizure frequency (65.6% in control group versus 91.7% in intervention group, RR 1.31, 95% CI 0.94 to 1.84, 4 trials; assumed risk 721 per 1000, corresponding risk 677 to 1000 per 1000). Acupuncture did not have excess adverse events compared to control treatment in the included trials.
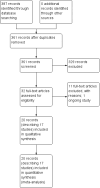
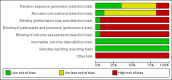
Authors' conclusions: Available RCTs are small, heterogeneous and have high risk of bias. The current evidence does not support acupuncture for treating epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures
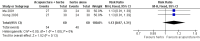
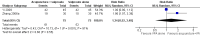























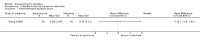



















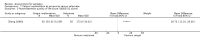







Update of
-
Acupuncture for epilepsy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 8;(4):CD005062. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005062.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 May 07;(5):CD005062. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005062.pub4. PMID: 18843676 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Deng 2001a {published data only}
-
- Deng Y, Wang J, Lin Y, Liu W, Wang L. Clinical observation on treatment of epilepsy general tonic‐clonic attack with catgut implantation at acupoint plus antiepileptic Western medicine of small dose. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2001;21(5):271‐3.
Han 2008 {published data only}
-
- Han D, Sun J, Zhuang L. Catgut embedding for treatment of 85 cases of generalized epilepsy. Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science 2008;24(6):35‐6.
Kloster 1999 {published data only}
-
- Kloster R, Lasson PG, Lossius R, Nakken KO, Dahl R, Zui‐Ling X, et al. The effect of acupuncture in chronic intractable epilepsy. Seizure 1999;8(3):170‐4. - PubMed
-
- Stavem K, Kloster R, Rossberg E, Larsson PLG, Dahl R, Kinge E, et al. Acupuncture in intractable epilepsy: lack of effect on health‐related quality of life. Seizure 2000;9(6):422‐6. - PubMed
Leng 2000 {published data only}
-
- Leng Y, Pan Q, Chen X, Yang T. Epilepsy treated by point thread embedding. Report of 86 cases. Journal of External Therapy of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2000;9(4):16.
Li 2007 {published data only}
-
- Li Y. Clinical research of treating generalized tonic‐clonic seizure with catgut embedding and medicine. Thesis (MPhil). Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2007.
Ma 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ma R, Zhang X, Liu Y, Li X, Yang C, Xiong J. Clinical observation on treatment of tonoclonic attack of infantile epilepsy with acupuncture plus Xi Feng capsule. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2001;42(5):276‐8.
-
- Zhang X. Clinical and experimental study on acupuncture combined with Xi Feng Jiao Nang for treatment of epilepsy of childhood. Thesis (MPhil). Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2000.
Mao 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mao ZN, Gao ZG, Zhang GW, Wang SB. Observation on therapeutic effect of acupoint catgut‐embedding combined western medicine for epilepsy of generalized seizures type. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2011;31(6):509‐12. - PubMed
Peng 2003 {published data only}
-
- Peng Y. Clinical study on treatment of infantile primary epilepsy with acupoint catgut‐implantation therapy. World Journal of Acupuncture‐Moxibustion 2003;13(1):38‐41.
-
- Peng Y. Studies of the clinic and experiment with embedding catgut in points to treat childhood primary epilepsy. Thesis (PhD). Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2000.
Shi 2001 {published data only}
-
- Shi J. Absence seizures of epilepsy treated by scalp acupuncture combined with hydro‐acupuncture at renying point. Report of 45 cases. Shaanxi Journal of Chinese Traditional Medicine 2001;22(1):43‐4.
Xiong 2003 {published data only}
-
- Xiong X, Zhang G, Huang W, Sun J. Clinical observation of acupuncture and Chinese medicine for treatment of epilepsy in children. Chinese Journal of Information on Traditional Chinese Medicine 2003;10(7):62‐3.
Yi 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yi H. Observation of electro‐acupuncture treatment of vasoconstriction district for grand mal seizures. Thesis (MPhil). Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2009.
Yu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Yu D, Ping X, Zhao X. Epilepsy treated by acupuncture with growing fluid and extinguishing wind. Report of 30 cases. Jiangsu Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1999;20(11):37.
Zhang 2006a {published data only}
-
- Zhang J, Li Y, Zhuang L. Clinical observation on catgut implantation at acupoint for treatment of generalised tonic‐clonic epilepsy. Report of 90 cases . Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2006;22(6):8‐10. - PubMed
Zhang 2006b {published data only}
-
- Zhang J. Study of curative effect of generalized tonic‐clonic seizure (GTCS) treated by catgut implantation at acupoint. Thesis (M. Phil.). Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2006.
Zhou 2000 {published data only}
-
- Zhou Y. Epilepsy treated by acupuncture with complementation with Yin and Yang. Report of 60 cases. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2000;41(7):441.
Zhuang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Zhuang L, Ding X, Chen M. Catgut embedding for treatment of epilepsy: observation of 22 cases. New Chinese Medicine 2004;36(1):46‐7.
Zhuang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zhuang Lx, Zhang J, Li YZ. Clinical observation on catgut implantation at acupoint for treatment of general paroxysmal epilepsy. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2006;26(9):611‐3. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Chui 2006 {published data only}
-
- Chui H, Pin J, Cao R. Catgut embedding and oral herbal medicines for treatment of 68 cases of epilepsy. Traditional Chinese Medicine Research 2006;19(9):61‐2.
Deng 2001b {published data only}
-
- Deng Y, Huang Z, Lin Y, Liu J, Huang L. Clinical observation on 88 cases of epilepsy with general tonicoclonic attack treated with medicated thread implantation at acupoint. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2001;42(7):406‐8.
Han 2005 {published data only}
-
- Han G, Han R. Catgut embedding for treatment of 800 cases of epilepsy. China's Naturopathy 2005;13(10):23‐4.
Kuang 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kuang K, Zhou D, Yu X. Clinical observation on 40 cases of epilepsy treated with acupuncture and Chinese herbs. Jiangxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1996;27(6):47.
Li 2004 {published data only}
-
- Li H, Zhang J. Catgut embedding in scalp acupoint for treatment of 112 cases of epilepsy. Journal of Clinical Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2004;20(6):46‐7.
Lin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lin J, Deng Q, Zhang J. Observation on therapeutic effect of 160 cases of epilepsy treated with acupoint catgut embedding therapy. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2001;21(11):653‐4.
Luo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Luo WP, Miao YN. Observations on the curative effect of combined acupuncture and medication on infantile hyperpyretic convulsion. Shanghai Journal of Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2004;23(7):12.
Wu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wu Y, Zou LP, Han TL, Zheng H, Caspi O, Wong V, et al. Randomized controlled trial of traditional Chinese medicine (acupuncture and tuina) in cerebral palsy: part 1‐‐any increase in seizure in integrated acupuncture and rehabilitation group versus rehabilitation group?. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2008;14(8):1005‐9. - PubMed
Xu 2003 {published data only}
-
- Xu Y, Zhang J, Deng Q. Acupoint catgut embedding therapy and its application in the treatment of epilepsy. Information on Tcm 2003;20(1):35.
Xu 2004 {published data only}
-
- Xu J, Lie X, Lie D. Acupuncture combined with herbal seizure tablet for treatment of epilepsy in children. Report of 64 cases. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2004;45(5):349.
Yi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yi G, Xiuyun W, Tangping X, Zhihua D, Yunchen L. Effect of blood‐letting puncture at twelve well‐points of hand on consciousness and heart rate in patients with apoplexy. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine = Chung i Tsa Chih Ying Wen Pan / Sponsored by All‐China Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2005;25(2):85‐9. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ChiCTR‐TRC‐10001023 {published data only}
-
- Zhao Y, Rong P. Ear‐acupuncture therapy for epilepsy. WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform: http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR‐TRC‐10001023 2010. [http://apps.who.int/trialsearch/Trial.aspx?TrialID=ChiCTR‐TRC‐10001023]
Additional references
Chen 1983
-
- Chen K, Chen G, Feng X. Observation of immediate effect of acupuncture on electroencephalograms in epileptic patients. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1983;3:121‐4. - PubMed
Commission 1989
-
- Commission on Classification and Terminology of the International League Against Epilepsy. Proposal for revised classification of epilepsies and epileptic syndromes. Epilepsia 1989;30:389‐99. - PubMed
Furlan 1999
Hauser 1993
-
- Hauser WA, Annegers JF, Kurland LT. Incidence of epilepsy and unprovoked seizures in Rochester, Minnesota: 1935‐1984. Epilepsia 1993;34:453‐68. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Holland 2001
-
- Holland KD. Efficacy, pharmacology, and adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs. Neurologic Clinics 2001;19(2):313‐45. - PubMed
Huang 1999
-
- Huang ZN, Yang R, Chen G, Cheng JS. Effect of electroacupuncture and 7‐NI on penicillin‐induced epilepsy and their relation with intrahippocampal NO changes. Sheng Li Xue Bao 1999;51(5):508‐14. - PubMed
Jansen 1989
-
- Jansen G, Lundeberg T, Kjartansson S, Samuelson UE. Acupuncture and sensory neuropeptides increase cutaneous blood flow in rats. Neuroscience Letters 1989;97:305‐9. - PubMed
Johansson 1993
-
- Johansson K, Lindgren I, Widner H, Wiklund I, Johansson BB. Can sensory stimulation improve the functional outcome in stroke patients?. Neurology 1993;43:2189‐92. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2009
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 (updated September 2009). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Liu 1995
-
- Liu J, Cheng J. Changes of amino acids release in rat's hippocampus during kainic acid induced epilepsy and acupuncture. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 1995;20(3):50‐4. - PubMed
Liu 1997
-
- Liu J, Cheng JS. Hippocampal non‐NMDA and GABA‐A receptors in benzylpenicillin‐induced epilepsy and electro‐acupuncture antiepilepsy. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao 1997;18(2):189‐91. - PubMed
Liu 2004
-
- Liu JH, Yan J, Yi SX, Chang XR, Lin YP, Hu JM. Effects of electroacupuncture on gastric myoelectric activity and substance P in the dorsal vagal complex of rats. Neuroscience Letters 2004;356(2):99‐102. - PubMed
Maciocia 1989
-
- Maciocia G. Foundations of Chinese Medicine: A comprehensive Text for Acupuncturists and Herbalists. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1989.
Magnusson 1994
-
- Magnusson M, Johansson K, Johansson BB. Sensory stimulation promotes normalization of postural control after stroke. Stroke 1994;25:1176‐80. - PubMed
Middlekauff 2004
-
- Middlekauff HR, Shah JB, Yu JL, Hui K. Acupuncture effects on autonomic responses to cold pressor and handgrip exercise in healthy humans. Clinical Autonomic Research: official journal of the Clinical Autonomic Research Society 2004;14(2):113‐8. - PubMed
NIH 1998
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. Acupuncture. JAMA 1998;280(17):1518‐24. - PubMed
Sander 1996
SCSSS 1999
-
- Swedish Collaboration on Sensory Stimulation in Stroke. Sensory stimulation after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1999;9 Suppl 1:1‐28.
Shi 1987
-
- Shi Z, Gong B, Jia Y, Hua Z. The efficacy of electroacupuncture on 98 cases of epilepsy. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1987;7:21‐2. - PubMed
Sun 2001
-
- Sun HL, Li XM. Clinical study on treatment of cerebral apoplexy with penetration needling of scalp acupoints [tou xue tou ci zhi liao nao zu zhong lin chuang yan jiu]. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2001;21(5):275‐8.
Wang 2001
-
- Wang G, Jiang N, He Z. Effects of scalp acupuncture on plasma ET‐1, MDA and NO contents in the patient of cerebral infarction. Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2001;21(4):241‐2.
Wu 1992
-
- Wu D. Mechanism of acupuncture in suppressing epileptic seizures. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1992;12:187‐92. - PubMed
Wu 1996
-
- Wu JN. A short history of acupuncture. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 1996;2(1):19‐21. - PubMed
Yang 1990
-
- Yang J. Treatment of status epilepticus with acupuncture. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 1990;10:101‐2. - PubMed
Yang 2000
-
- Yang R, Huang ZN, Cheng JS. Anticonvulsion effect of acupuncture might be related to the decrease of neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthases. Acupuncture Electrotherapy Research 2000;25(3‐4):137‐43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

