Induction of protective effector immunity to prevent pathogenesis caused by the respiratory syncytial virus. Implications on therapy and vaccine design
- PMID: 24801878
- PMCID: PMC4137950
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12313
Induction of protective effector immunity to prevent pathogenesis caused by the respiratory syncytial virus. Implications on therapy and vaccine design
Abstract
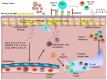
Human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) is the leading cause of respiratory illness in infants and young children around the globe. This pathogen, which was discovered in 1956, continues to cause a huge number of hospitalizations due to respiratory disease and it is considered a health and economic burden worldwide, especially in developing countries. The immune response elicited by hRSV infection leads to lung and systemic inflammation, which results in lung damage but is not efficient at preventing viral replication. Indeed, natural hRSV infection induces a poor immune memory that allows recurrent infections. Here, we review the most recent knowledge about the lifecycle of hRSV, the immune response elicited by this virus and the subsequent pathology induced in response to infection in the airways. Novel findings about the alterations that this virus causes in the central nervous system and potential therapies and vaccines designed to treat or prevent hRSV infection are discussed.
Keywords: T helper type 1/type 2 cells; hRSV; lung; vaccination; viral.
© 2014 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Blount RE, Jr, Morris JA, Savage RE. Recovery of cytopathogenic agent from chimpanzees with coryza. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956;92:544–9. - PubMed
-
- Beem M, Wright FH, Hamre D, Egerer R, Oehme M. Association of the chimpanzee coryza agent with acute respiratory disease in children. N Engl J Med. 1960;263:523–30. - PubMed
-
- Chanock R, Finberg L. Recovery from infants with respiratory illness of a virus related to chimpanzee coryza agent (CCA). II. Epidemiologic aspects of infection in infants and young children. Am J Hyg. 1957;66:291–300. - PubMed
-
- Nair H, Brooks WA, Katz M, et al. Global burden of respiratory infections due to seasonal influenza in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2010;378:1917–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

